Have you ever wondered why Google keeps pumping out algorithm updates?
Do you understand what Google algorithm changes are all about?
No SEO or content marketer can accurately predict what any future update will look like. Even some Google employees don’t understand everything that’s happening with the web’s most dominant search engine.
But think about it like this: Search engines are built to serve people.
People change. Plain and simple.
And as our behavior changes, technology evolves to keep up with our wants and needs.
So, search engines have to change too.
For example, a decade ago, we didn’t have social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest to help funnel traffic to our sites.
We also didn’t think twice about mobile traffic or best practices for reaching searchers that were on the move because those millions of searchers didn’t exist.
Fast forward to present day where marketing trends seem to change overnight. New tools and technology emerge at a moment’s notice.
Because of this, Google regularly tweaks how they treat rankings, links, and especially content in the wake of these rapid changes.
But at the core of Google’s algorithm changes is a simple goal: provide the best user experience possible.
Given that Google handles over 2 trillion searches per year (that’s about 40,000 every second), even the smallest changes to their algorithm can have a massive impact on any given site.
Your site, my site, you name it.
And content marketers have a lot to keep up with when you consider the 200 ranking factors outlined by Google.
Yes, two hundred.
There are some factors which are effectively out of our control, such as the ages of our sites and domain names.
However, many of these ranking factors are within our control. These are mostly related to unique content, on-page optimization, and choice of links. Essentially, we do have a hand in how Google treats our sites’ search rankings.
Simply put, sites that stay on Google’s good side are more likely to rank. Those who try to play the system suffer punishment in one way or another.
Thankfully, Google is fairly transparent about how they can help sites rank. On the flip side, there are some “hidden” aspects of Google’s algorithm updates that can hit unsuspecting sites.
And that’s exactly why I’ve created this in-depth guide.
Google has issued five major algorithm updates, named (in chronological order) Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, Pigeon, and Fred. In between these major updates, Google engineers also made some algorithm tweaks that weren’t heavily publicized but still may have had an impact on your website’s rankings in the search results.
Below, I’ve broken down each and every one of the major Google algorithm changes piece by piece.
Worried that you might be doing something wrong in the eyes of Google?
Want to know how to bounce back from a penalty?
You’ve come to the right place.
Google Algorithms and Why They Change
Before you can fully understand the impact of each individual search algorithm update, you need to have a working knowledge of what a search engine algorithm is all about.
The word “algorithm” refers to the logic-based, step-by-step procedure for solving a particular problem.
In the case of a search engine, the problem is “how to find the most relevant webpages for this particular set of keywords (or search terms).”
The algorithm is how Google finds, ranks, and returns the relevant results.
Google is the #1 search engine on the web and it got there because of its focus on delivering the best results for each search.
As Ben Gomes, Google’s Vice-President of Engineering, said, “our goal is to get you the exact answer you’re searching for faster.”
From the beginning, in a bid to improve its ability to return those right answers quickly, Google began updating its search algorithm, which in turn changed – sometimes drastically – the way it delivered relevant results to search users.
As a result of these changes in the algorithm, many sites were penalized with lower rankings while other sites experienced a surge in organic traffic and improved rankings.
Some brief history: Algorithm changes can be major or minor. Most of them, however, are minor.
In 2014, Google made approximately 500 changes to the algorithm. After each of those tweaks, a large number of sites lost their rankings.
Ten years earlier, in February 2004, Google issued the Brandy update.
A major algorithm change, Brandy’s major focal points were increased attention on link anchor texts and something called “Latent Semantic Indexing” – basically, looking at other pages on the same site to evaluate whether they contain the search terms, in addition to the indexed page.
Eventually, Google’s focus shifted to keyword analysis and intent, rather than solely looking at the keyword itself.
Going back even further, Google made a number of changes in 2000, including the launch of the Google toolbar and a significant tweak known as “Google Dance.”
However, as far as SEO’s impact on business websites is concerned, those updates didn’t have much impact on search results.
If you want to be up-to-date on these algorithm changes, you can review the entire history of Google’s algorithm changes.
Google needs large volumes of data to be able to make better decisions for any rank tracker. The more relevant results people get when they search for a specific keyword, the more accurate the data that Google can extract and return for other searchers.
That’s why these changes have also impacted mobile search results.
As I already pointed out, Google wants to do good by their users.
They want their search results to make sense, and the job of their algorithm is to reward the sites in the SERPs that deliver what users want.
After all, the company’s focus on user experience is exactly why they won the search engine wars against competitors such as Yahoo!, Lycos, and Bing.
Google also prides themselves on being the “good guy” of the Internet, and their search algorithm confirms this.
The company’s old corporate motto of “Don’t be evil” is a stark warning for sites who try to game their system.
When we look at some key search algorithm changes over the years, it’s clear how Google’s desire to do good shines through.
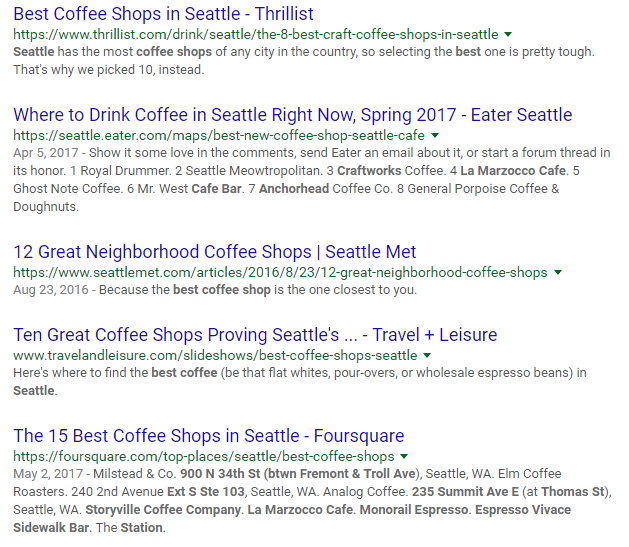
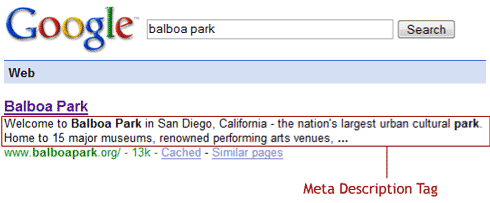
Perhaps the most obvious example of Google altering their algorithm to assist users was the phenomenon of exact match domains a few years back.
In the not-so-distant past, the top results in the SERPs were brimming with spammy sites like “BestCoffeeShopSeattle.com.” Sites like this often outranked branded domains (think: Starbucks) or other more relevant results.
Sites like these were the bread and butter of affiliate marketers, often subject to keyword stuffing and other shady search tactics.
Deciding enough was enough, Google decided to put their foot down.
Long story short, Google punished spammy exact match sites. The result of their algorithm change looks something like this when we search for “best coffee shop Seattle:”
No spam, just real results for actual coffee shops. That’s Google’s algorithm at work.
Sure, it’s a bit scary to think that Google could potentially wreak havoc on your rankings at any given moment on a whim, right?
But it is necessary considering their objective of delivering the best user experience possible.
I’ve helped clients and friends in the past with algorithm penalties and have seen firsthand what happens when Google comes down hard on a site.
Trust me, it’s not pretty.
But don’t think of these algorithms as twisting your arm. The best long-term search strategy for anyone looking for traffic (even me!) is to align themselves with Google’s goals.
The better you understand the history of Google’s algorithms, the more likely you are to run a site that ranks well.
In this article, we’ll focus on five major Google search algorithm changes. Each of these updates had and continues to have, a significant impact on search engine marketing, on-page SEO, and your site’s overall content strategy for best search results. Specifically, we’ll discuss:
The Core SEO Benefits of Google Algorithm Changes
In the last couple of years, we’ve seen the positive impacts of the Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, Pigeon, and Fred algorithm updates on SEO. Some of these benefits include:
Google’s user-focused commitment – Remember Google’s goal: to help each search user find the correct information they’re looking for as quickly as possible. These updates, especially Panda, further solidify Google’s commitment to their users.
Although there is still a lot more work to be done by Google to improve search results, the odds are good that you’ll get relevant and informative results on the first page of results from Google when you search.
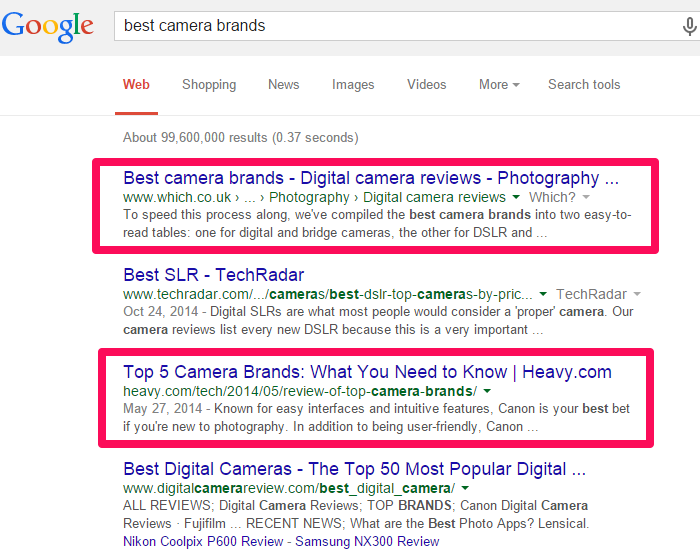
For example, let’s say you search for best camera brands. Your top results will likely include those search terms, or their closest synonyms, in close proximity to each other:
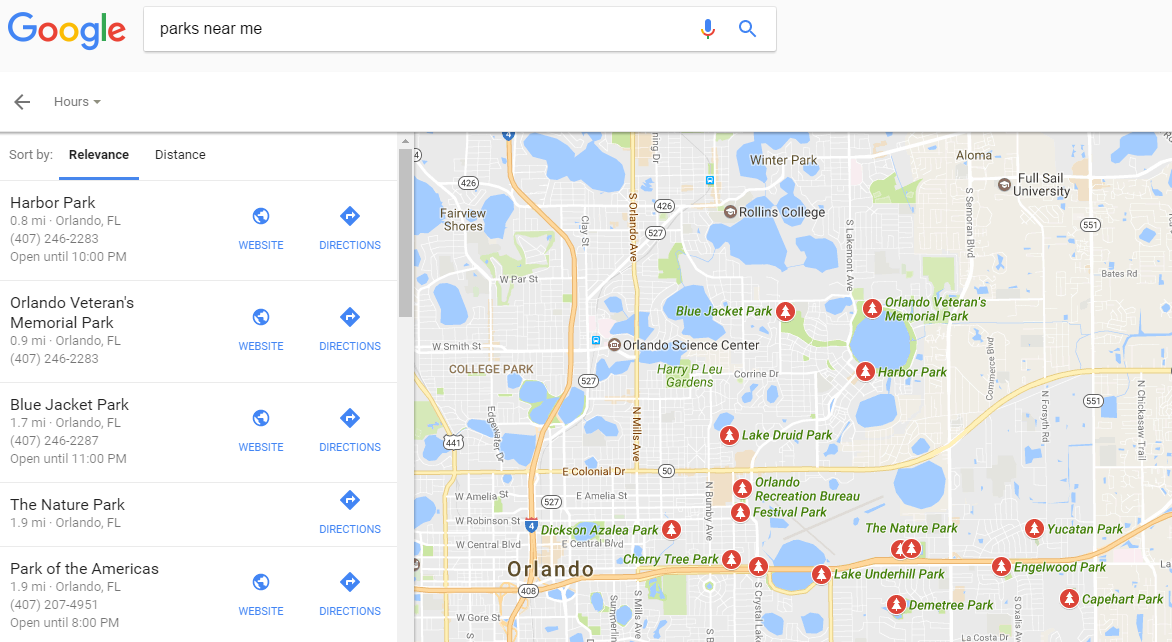
Google also recognizes the need to meet the needs of those searching on-the-go. For example, searchers no longer need to explicitly state keywords if they’re looking for something locally. “Near me” is good enough for Google granted you’ve provided your location.
This update was a game-changer for sites relying solely on local keywords and ultimately makes life easier for users.
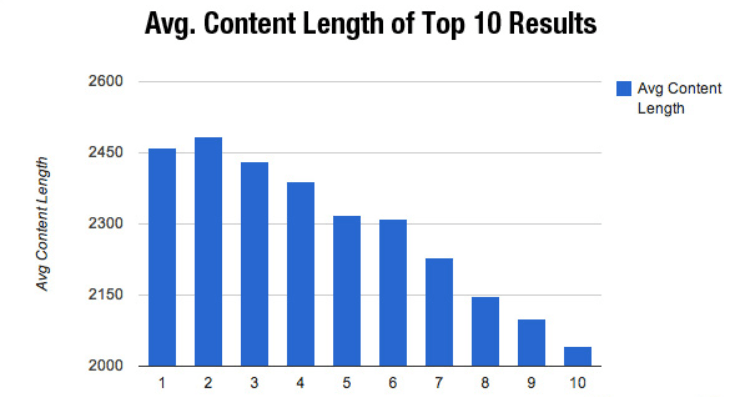
Improved rankings for in-depth content – serpIQ agrees that “length is strength” in modern SEO.
Longer content tends to dominate search engine results pages these days in SEO power.
Prior to Google Panda, thin content could, and often did, rank highly.
Content writers could churn out 300 words per article or blog post, throw in some high PR links and wind up ranked #1 in Google – and remain there for months.
The Panda changed that. Those days are over, so post long content if you want to improve your rankings, says Brian Dean.
Content farms (sites that frequently generate and quickly publish low quality and thin content) were the major culprits.
Sites like EzineArticles, ArticleAlley, and Buzzle lost their rankings even though they had aged domain names and were mobile friendly. Their content couldn’t provide meaningful, relevant, long-term solutions with lasting SEO power.
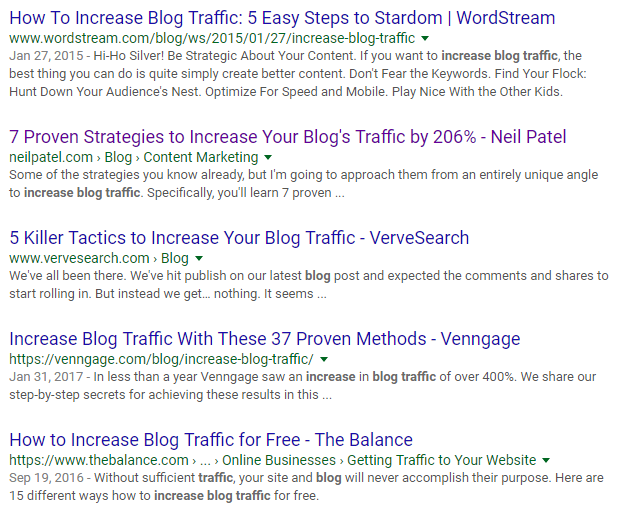
These days, Google gives preference to in-depth pieces of content that are likely to remain useful. For example, one of the articles from this blog is sitting at #2 for an in-demand keyword phrase (“drive traffic to blog”):
When we talk about “in-depth content,” we’re usually talking about “how-to” pieces that educate your readership. They’re the sort of pieces that help marketers position themselves as problem solvers.
Heck, the article you’re reading now is an example of in-depth content.
Crafting this sort of long-form content represents a win-win situation for marketers, which is why all of my blog posts are well over 2,000 words and focus on solving problems.
For example, Brian Dean absolutely kills it with his in-depth pieces.
His SEO guides regularly receive thousands of shares and comments because they deliver actionable advice that is relevant to his readers.
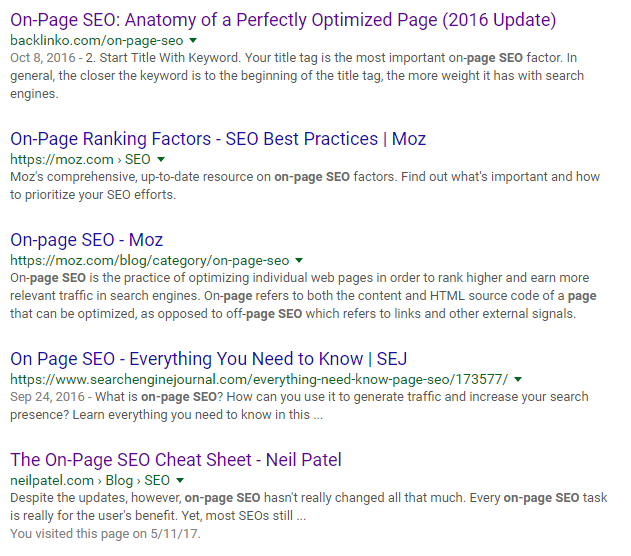
Brian’s site is rewarded for his hard work, too. Check out the top Google results for “on-page SEO” (and notice that I’m not too far off myself!):
But just as Google rewards in-depth content, they punish thin or questionable content.
This sort of content often falls into two categories:
- Short-form, keyword-stuffed pieces crafted for the sole purpose of ranking
- Content with questionable backlink profiles, such as paid links or private blog networks (networks of sites artificially linking to each other for the purpose of improving rankings)
Google took a sledgehammer to sites relying on thin content thanks to the Panda and Penguin updates.
The traffic of many “niche” sites using PBNs tanked almost overnight due to algorithm changes, as noted by Spencer Haws of Niche Pursuits:
You can’t rely on shortcuts and cheap tricks if you want to rank in 2017 and beyond. The key takeaway here isn’t to live in fear of Google, but rather craft content that people actually want to read.
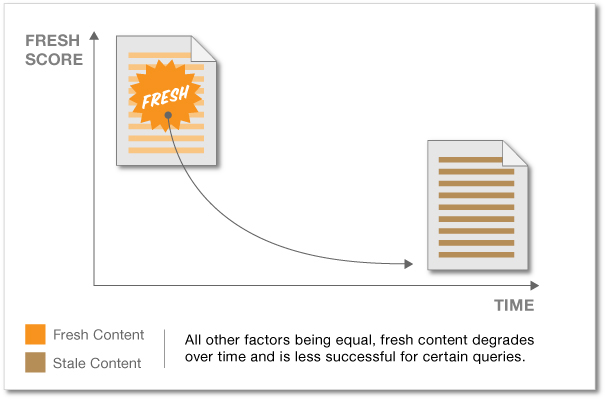
Fresh content advantage – When you publish fresh content on your site, Google gives your webpage a score. Over time, this freshness score will fizzle out, and your site will require more fresh content. This is where a website auditor helps keep you fresh.
Cyrus Shepard notes that “the freshness score can boost a piece of content for certain search queries,” even though it then degrades over time.
The freshness score of your web page is initially assessed when the Google spider crawls and indexes your page.
Therefore, if you’re always updating your blog or site with relevant, well-researched, and in-depth (2,000+ words) content, you should expect improved rankings and organic visitors from Google.
By the same token, sites that publish sporadically will find it hard to retain a solid position in Google.
Most of the popular sites post new content at least once a week.
Some sites, like Moz, publish every day. They will often use something like SEO Powersuite as an internal website auditor to stay ahead of the competition.
In order to continually boost the freshness score, some popular brands, like Mashable, publish several pieces of detailed content on a daily basis.
Brand awareness – This may not be obvious, but the Google algorithm changes support a shift towards branding.
Before Google started penalizing sites that use a lot of keyword-rich anchor text for internal links, over-optimization used to work. But, SEO has evolved and building links shouldn’t be the major focus (even though it’s important).
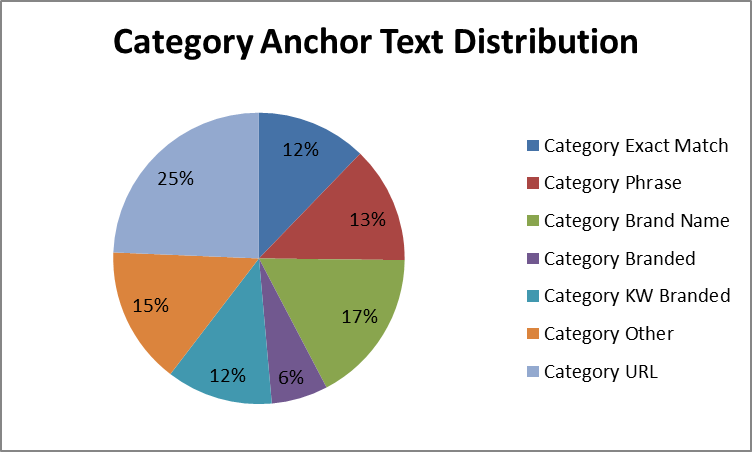
Moz recommends that 17% of your anchor text should be brand names.
Corporate organizations, small business owners, and bloggers have become meticulous when using anchor text.
Build links that will improve your brand and relevance online, and avoid building links to artificially boost your organic rankings.
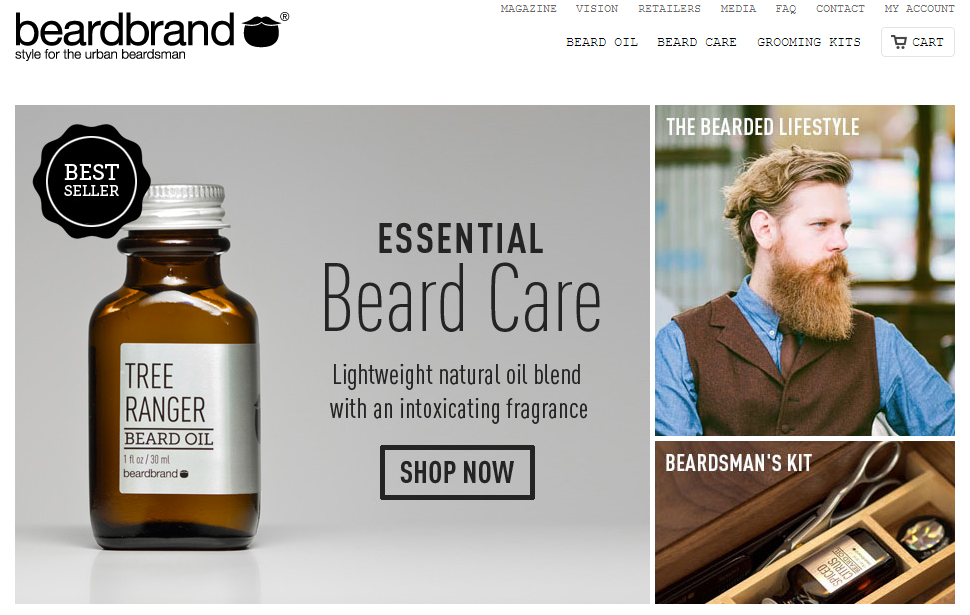
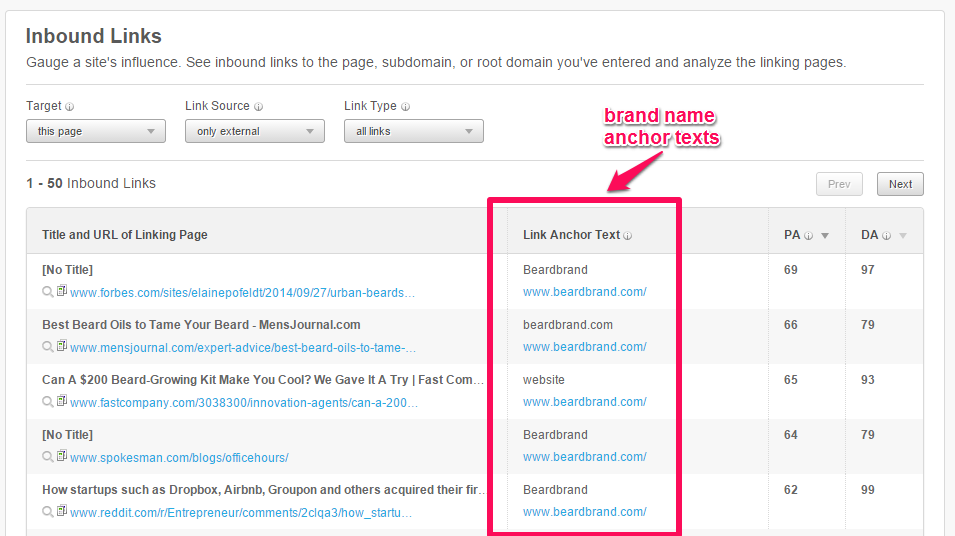
Look at BeardBrand.com. Their major keyword (best beard oil) is currently on the first page of the Google results in a rank tracker.
Many of their anchor text phrases contain brand names and domain URLs. This is the result I got from OpenSiteExplorer:
Major Google SEO Algorithm Changes and Penalties
Despite popular belief, Google’s algorithm is constantly changing. While we often discuss major milestones in the algorithm such as Panda and Penguin, Google rolls out smaller updates and penalties to supplement the larger ones.
Moz notes three updates and penalties took place between January and March 2017 alone. For example, Google introduced a penalty immediately after the 2017 New Year to combat aggressive ads on mobile sites.
Google actually hinted at the update months in advance, which doesn’t happen often. In fact, Google provided specific examples of what marketers shouldn’t do if they want to avoid a penalty for their mobile sites.
The lesson here is that Google’s algorithm doesn’t suddenly transform in a single day or update. Minor changes in the algorithm occur much more often than major ones.
But it’s the major updates (Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, Pigeon, and Fred) which represent the game-changers that all SEOs and content marketers must be aware of.
And before we get into the specifics of the updates themselves, I’m going to show you my method on how to analyze the updates as they apply to your site.
Signs That You’ve Been Penalized by a Google Algorithm Change: So, with so many moving pieces to Google’s algorithm, how do you actually figure out if you’ve been penalized?
If your site suffers from any of the following four symptoms, you might be on the receiving end of a slap on the wrist from Google.
Rank Demotion and Organic Traffic Drop: Perhaps the most obvious sign of a penalty is a sudden drop in your site’s ranking in the SERPs.
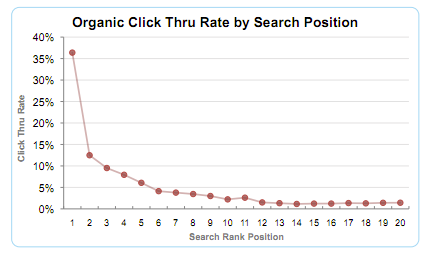
If your site gets pushed off the first page of Google for a term, for example, your site’s traffic will feel the effects almost immediately. Considering that the top results in organic search receive approximately 35% of clicks, a rank demotion could be potentially catastrophic.
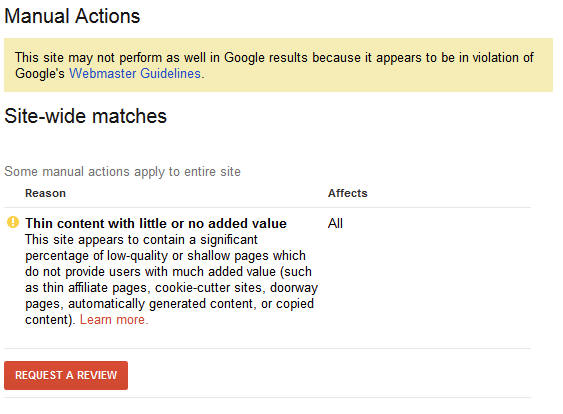
Manual Rank Change – In most cases, Google’s algorithm does most of the legwork when punishing pages.
However, Google does take manual action against sites from time to time if they suspect that you’re up to no good.
Luckily, Google will typically notify you if they think that something’s fishy. After all, accidents happen, and Google doesn’t want to needlessly punish unsuspecting sites. As long as you avoid black hat SEO techniques, you’re likely safe from being manually punished.
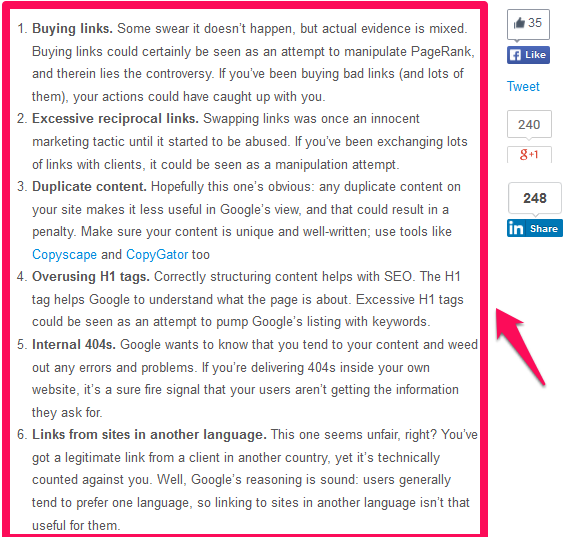
Banned by Google – If Google decides to blacklist your site, you probably know that you’ve done something seriously shady such as buying links, spamming directories, or excessive keyword stuffing.
Or you’ve done something legitimately illegal like distribute a virus or malware on-site.
Google’s not afraid to bring the hammer down on sites engaging in illicit activity. Those looking for SEO shortcuts should tread lightly if they want to avoid a potential penalty.
Thankfully, you can recover from penalties as a result of Google SEO algorithm changes.
But first, you need to know exactly which penalties you’re facing.
How to Determine Which Google Algorithm Penalties You’ve Been Hit With
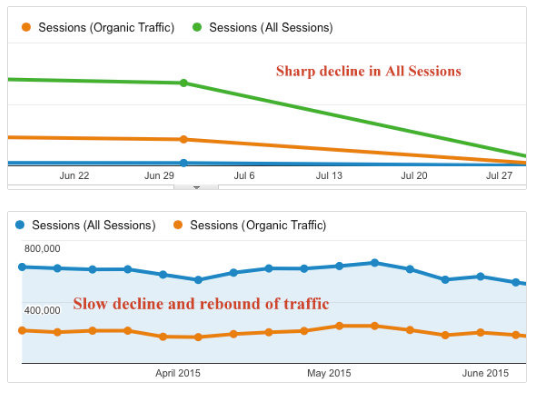
If you keep a close eye on your Google Analytics, you’ll be able to tell if you’ve been hit with a penalty. For example, a steep drop in traffic could signal that something’s wrong.
Now, keep in mind the difference between a sharp decline in traffic versus a slow decline that rebounds. If you’ve been penalized, your traffic is likely to go down and stay down.
Once you’re aware of your potential penalty, it’s time to figure out exactly what’s wrong. Chances are you can match your penalty with a particular update based on the timing of your traffic’s decline.
Google lends a helping hand to penalized site owners through its Webmaster Tools platform.
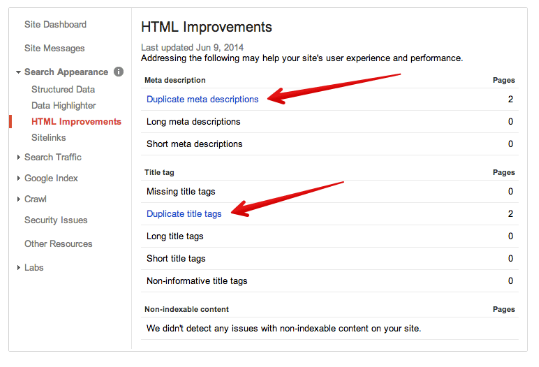
For example, Webmaster Tools can help you diagnose problems such as a potential duplicate content penalty.
If you’ve already installed the platform, simply log in, select Search Appearance and then HTML Improvements in the drop-down menu. Google then provides a list of any potential issues and allows you to take the necessary actions to fix them.
As noted, not all algorithm penalties are identical in terms of severity. In fact, Google changes their algorithm hundreds of times per year. In other words, there’s a good chance that a site could be penalized due to factors beyond a major update.
Now, let’s talk about the specific algorithms themselves.
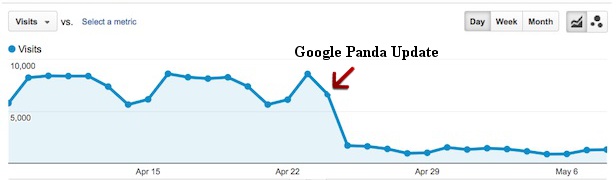
Google Algorithm Update: Panda
You’ve probably heard of Panda. But, unless you’re a veteran SEO expert who consumes Google-related news on a daily basis, you may not be intimately familiar with its details.
The Google Panda update revolutionized SEO, prompting every business that relies on Google for lead generation and sales to pay attention.
One important lesson that we’ve learned is that SEO is never constant. It’s continuously evolving and today’s “best practices” can become outdated tomorrow. After all, who would have believed that exact match domain names would ever be penalized by Google?
What Is the Panda update? Panda uses a search algorithm named after the Google Engineer, Biswanath Panda.
In February 2011, the first search filter that was part of the Panda update was rolled out. It’s basically a content quality filter that was targeted at poor quality and thin sites with little SEO power in order to prevent them from ranking well in Google’s top search engine results pages (SERPs).
Whenever a major Panda update happened, site owners noticed either a drop in organic traffic and rankings or a boost.
It changed content strategy, keyword research, and targeting. It even changed how links are built since high-quality relevant links pointing to a webpage ultimately add to its value when it comes to SEO power.
Google could now determine more accurately which sites are “spammy” and which sites would likely be deemed useful by visitors.
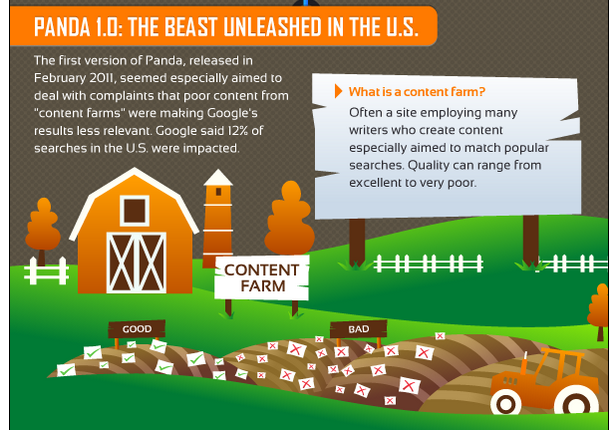
Before Panda, poor content could rank quite highly or even dominate Google’s top results pages. Panda 1.0 was unleashed to fight content farms. Google said the update affected 12% of searches in the U.S.
Note: Panda is called an update because the filter runs periodically. And, every time it runs, the algorithm takes a new shape.
In other words, high-quality content will likely bounce back in the search results while content pages that escaped the previous update get caught in the Panda net.
There has been a Panda update every 1-2 months since 2011, for a total of 28 updates with the most recent in May of 2015. This number may not be precisely accurate, because a lot of minor tweaks most likely have occurred in-between them, but it lies within that range.
1) Panda 1.0 update: The search filter was aimed at content farms — those sites that employ many writers who create poor-quality content around specific keywords in a bid to rank in Google’s top ten results on a rank tracker. This update was primarily aimed at U.S. sites and affected 12% of search results.
However, this doesn’t mean that all multi-author sites are spammy. For example, Moz has hundreds of writers, but it still enjoys top rankings in Google, because it makes sure that the content delivers plenty of value to readers.
In other words, in-depth content that is well researched and that gets shared on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, Google+ and the other major social platforms continues to rank well – perhaps even more highly than before.
2) Panda 2.0 update: This update, released in April 2011, targeted international search queries, though it also impacted 2% of U.S. search queries.
This filter also affected international queries on google.co.uk and google.com.au and English queries in non-English speaking countries e.g. google.fr, google.cn, when the searchers chose English results.
Amit Singhal, who is in charge of search quality at Google, told Vanessa Fox that Google was “focused on showing users the highest quality, most relevant pages on the web.”
3) Panda 2.1 – 2.3: There were minor updates in May, June, and July 2011 (dates approximate), in which Google incorporated more signals to help gauge the quality of a site.
Low-quality content and pages were further penalized, while those who worked extremely hard at producing rich and interesting content saw a boost in organic traffic when looking at the rank tracker.
Panda 2.3 was minor and focused on the user experience. Bloggers and site owners who wrote and published content that engaged the user and enhanced site navigability benefited from these changes according to any website auditor.
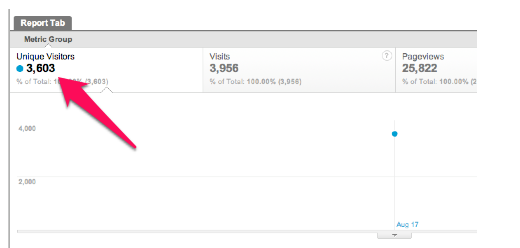
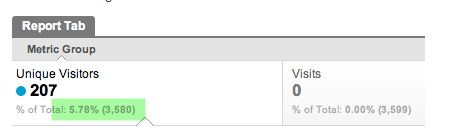
4) Panda 2.4: This update was rolled out on August 12th, 2011 and affected about 6-9% of user queries. It focused on improving site conversion rates and site engagement, says Michael Whitaker.
Prior to the update, Michael Whitaker was getting up to 3,000 unique visitors to his site.
As soon as the Panda 2.4 update was rolled out, his monthly site traffic dropped to 207.
5) Panda 3.0: This SEO power search filter began to roll out on October 17, 2011 and was officially announced on October 21, 2011. This update brought large sites higher up in the SERPs – e.g., FoxNews, Android.
After Panda 2.5, Google began to update their algorithm more frequently. This term is called “Panda Flux”.
To be on the safe side with your content, Express Writers recommends the following steps:
6) Panda 3.1 went live on November 18, 2011. It was minor and affected about 1% of all search queries. Although this number seems low, it is still significant for any rank tracker, considering the number of searches conducted every day.
Each of these algorithm changes came about as a result of search users not getting relevant and useful information. As an advertising media company, Google wants to make money, and unless they satisfy searchers, how would they do that?
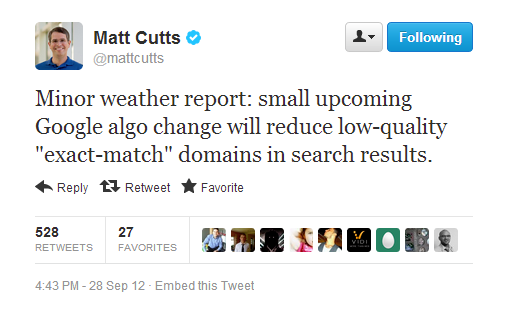
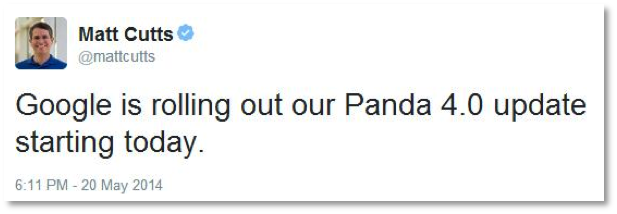
7) Panda 4.0: On May 20, 2014, Matt Cutts tweeted that Google was rolling out Panda 4.0. It was the next generation of Panda, and it generated both winners and losers.
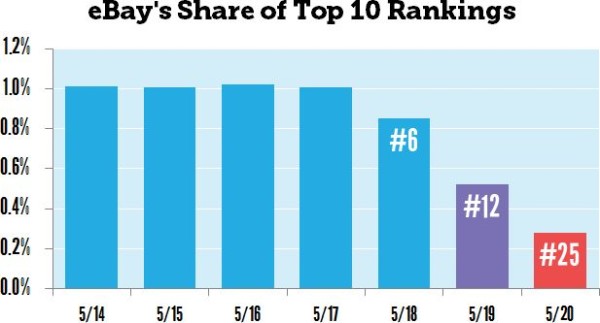
This update had a big impact. Ebay lost a significant percentage of the top 10 rankings it had previously enjoyed.
Panda 4.0 was primarily targeted at larger sites that have been dominating the top-10 results for seed keywords.
When you build a site today, you have to consistently write and publish in-depth content. This content must add value, be interesting to the reader, and solve a definite problem with availability on mobile devices.
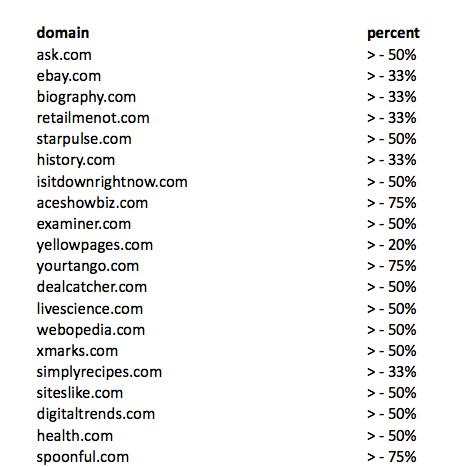
If you fail to do that, you won’t engage readers and your conversion rate will be low. The major losers after Panda 4.0 rolled out were:
As with every Panda update, there are winners too. Here’s a list provided by Search Engine Land:
Overall, not every sector or industry lost in Panda 4.0. The major ones worth noting were:
With Panda 4.1, Google once against laid the gauntlet down against keyword stuffing, rolling out an update that impacted between 3-5% of search queries.
The latest update, Panda 4.2, was introduced in May 2015. There haven’t been many significant changes to Panda since 4.0. However, there were some stories of sites managing to bounce back after cleaning up their content in the midst of Panda 4.1.
Think of Panda as “the content update.” Simply put, Google looked to bring an end to the era of article spinning and low-effort content. For the most part, the update was a success for encouraging marketers to focus on valuable, thought-provoking pieces versus fluff.
Again, this all ties back to Google’s desire to emphasize user experience. Rather than let marketers get away with spammy and misleading results, Google fought back.
Factors That Led to a Panda Penalty (and How to Fix Them)
Since some sites experienced a boost in organic rankings and traffic, it’s worth asking: What makes a site vulnerable to a Panda attack? Here are six factors that may be to blame along with suggestions as to how to fix the underlying problem and get back in Google’s good graces when using your website auditor:
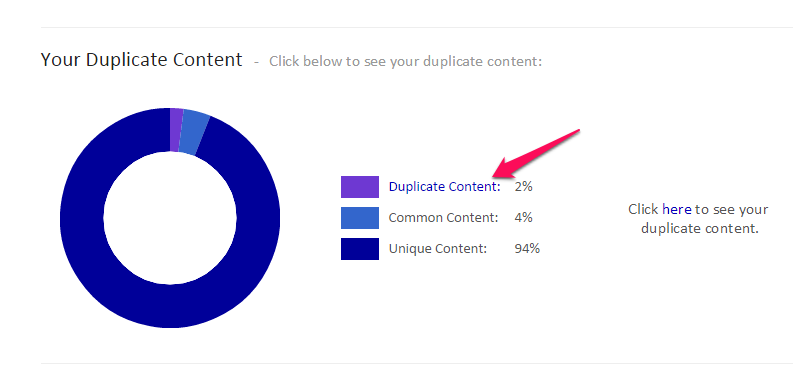
Duplicate content – Do you have substantial blocks of content that are the same on your site? This can cause a lot of problems, especially where SEO is concerned, but for site visitors, too.
In this video, Matt Cutts explains that duplicate content per se may not affect your site, except when it’s spammy:
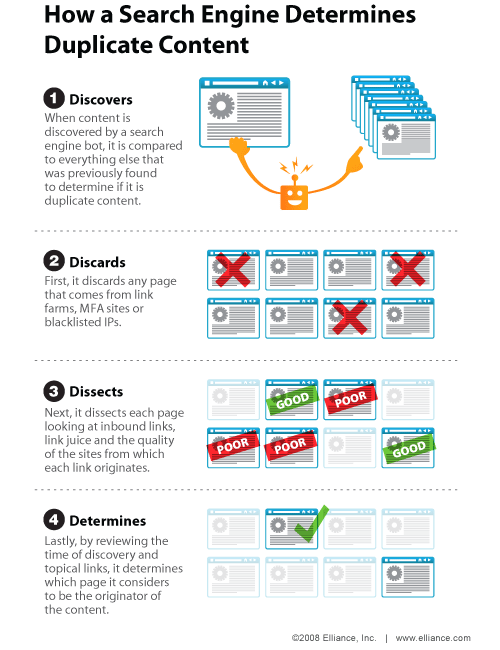
It’s not advisable to redirect duplicate pages. When the Google spider discovers duplicate content on your site, it will first analyze other elements that make up your web page before penalizing you.
Thus, it’s recommended that you completely avoid any form of content duplication and focus on publishing unique, helpful, and rich content for SEO power. Don’t be deceived: There is no balance between original and duplicate content.
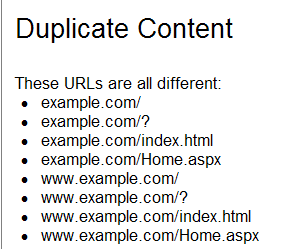
When the same content appears across your domain names and URLs, it could trigger a problem.
Some time ago, Greg Grothaus explained why this is a problem by sharing the image below. Since the content is the same, though the URLs are slightly different, Google “thinks” you have duplicate content.
Fortunately, finding duplicate content on your site is fairly easy to do. Simply follow these steps:
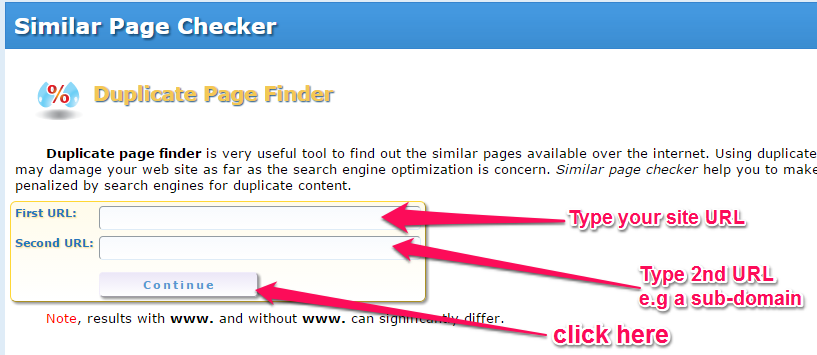
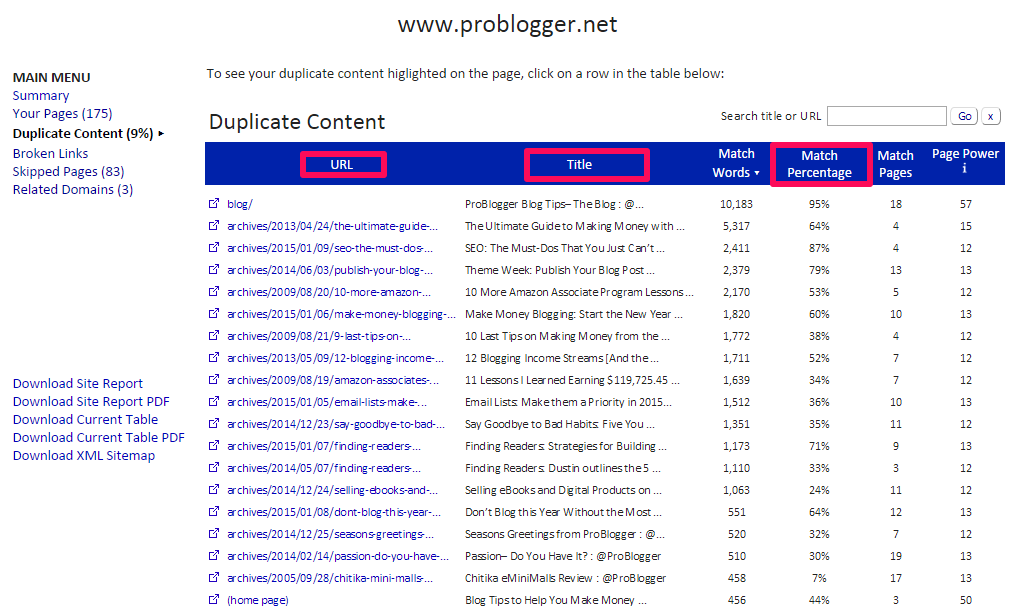
Step #1: Visit the Duplicate Page Finder tool. Input your site URL. Input another URL that you want to compare for duplicate content – e.g., yoursite.com/about.
Step #2: Analyze your results. If the results show that your pages contain some duplicate content, you can then solve the problem in one of two ways:
- Revise one of the pages so that each page contains 100% original content
- Add a no-index tag, so that the Google spider will ignore it and not index or pass link juice to it helping on the rank tracker.
Another problem that can trip you up is where your content is duplicated on someone else’s site. To find duplicate content outside your site, follow these steps:
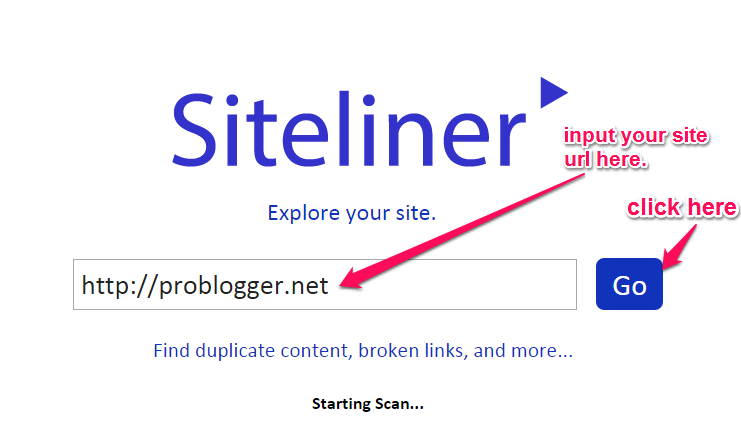
Step #1: Go to Siteliner.com. Plug in your site URL and hit the “Go” button.
Step #2: Analyze duplicate content pages. On the results page, scroll down and you’ll find the “duplicate content” results.
Once you’ve clicked the “duplicate content” link, you’ll get a list of all of the pages that you need to make unique and will be told by how much.
If you accept guest posts or sponsored articles on your blog, you should make it a habit to check for duplicate content first.
The moment you receive the content, quickly run it through any one of the many duplicate content/plagiarism checker tools available on the web – e.g., smallseotools.com.
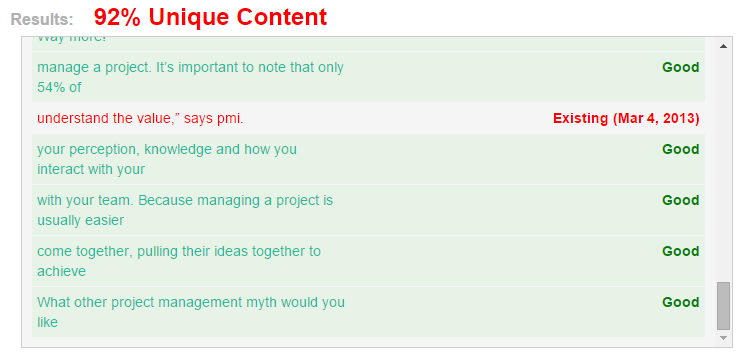
After running your content through the tool, you’ll see an analysis of the piece’s unique vs. duplicate phrases, sentences, and paragraphs.
Note: Looking at the screenshot above, we see that the results specify 92% of the content is unique. That’s a fairly decent score and one you can live with.
However, if the piece you’re checking scores between 10 to 70% unique content, you should either improve it or take it down. Excessive duplicate content can result in a Google penalty for your site’s SEO power when the next Panda update is rolled out.
It’s also very important to note that just because you have 100% unique content on your site, that doesn’t automatically mean higher rankings for you.
Oftentimes it’s backlinks which represent the strongest signal to Google that your on-site content is valuable. According to a 2015 Moz study on backlinks, there’s a massive correlation between higher rankings and the number of external links from unique sites.
As noted by Moz’s Cyrus Shepard: “If you want to rank for anything that’s even remotely competitive, the chances of finding a website ranking without external links is very rare indeed.”
However, it’s no longer about having the “most” backlinks. In this post-Penguin era, it’s also about having trusted and relevant backlinks.
Lastly, perhaps the best way to avoid duplicate content is to follow this simple rule:
When in doubt, write original content.
Nobody wants to read a blog post that’s been published and revised thousands of times before.
Not only does crafting original content prevent you from repeating what someone else has already said, but also provides opportunities for you to answer questions for your audience that nobody else is bothering to touch.
Low-quality inbound links – If you’ve discovered that your SEO is tanking and you’re confident that your site content is both useful and unique, the next step is to audit your inbound links.
Low-quality links pointing to your pages can also trip you up because Penguin 2.1 was all about putting the search engine focus on quality over quantity.
According to Kristi Hines, any low-quality content from the past can come back to haunt you. So, it’s not enough to begin building good, high-quality links today. The ones that you built when you first started marketing can also have an effect in any rank tracker.
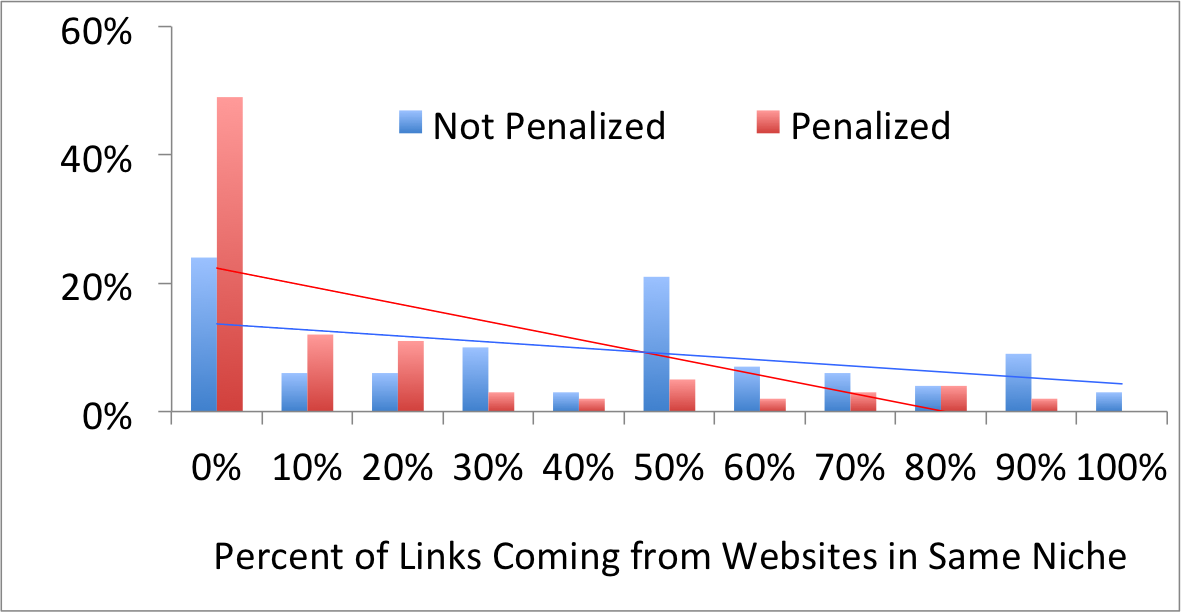
The ugly truth is this: If your site has a large number of inbound links coming from irrelevant sites (i.e., content farms or sites in a different niche altogether), your chances of getting a Google penalty increase.
You need to focus on getting incoming links, predominantly from sites that have the same theme or subject as your site. The SEM Blog chart below gives us a clearer picture.
But before you can do anything about those low-quality links, you first need to find them.
In other words, you need to find out how many backlinks you have built or gained over the course of your site’s existence. Fortunately, becoming this type of website auditor is fairly simple. Just follow these steps:
Step #1: Go to OpenSiteExplorer. Type in your site URL. Hit the “Search” button.
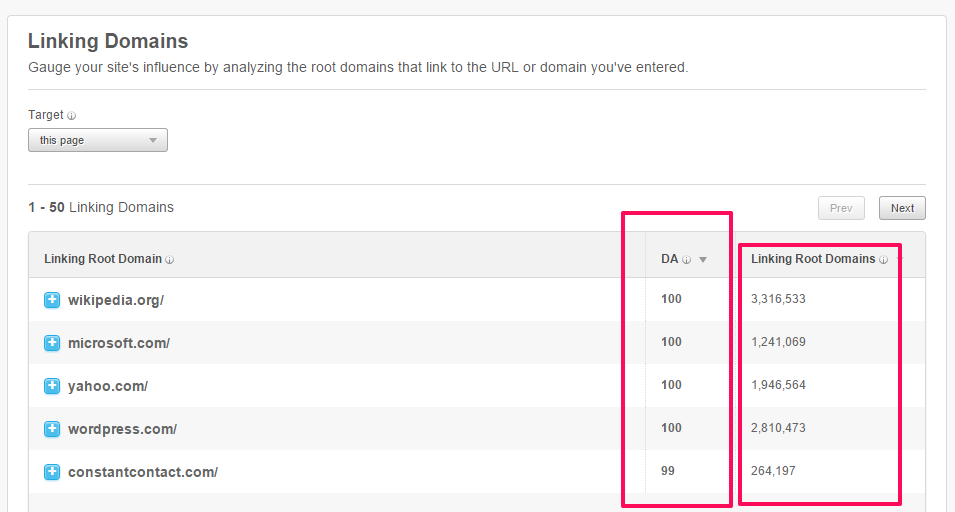
Step #2: Click on “Linking Domains.”
Step #3: Analyze the linking domains.
You can find toxic links on your own page in several places. Links in your page footer, site wide links, and links with over-optimized anchor text, among others, are all good places to start.
Listen: If you think that inbound links aren’t your responsibility, think again. Although you can’t necessarily control who chooses to link to your site, paying close attention to your link profile can save you a major headache down the road.
For example, bad backlinks can actually damage your search rankings if you don’t deal with them before they get out of control. Rather than look suspicious to Google, keeping your link profile squeaky clean on a regular basis keeps you from having to play catch-up or fact a potential penalty.
If you need more information about remedying either of these first two Panda-penalty factors – duplicate content and low-quality inbound links – try these helpful articles:
- How To Identify and Remedy and Duplicate Content Issues on Your Website
- How To Find Low-Quality Inbound Links with Buzzstream
High bounce rate – The term “bounce rate” simply refers to how many single-page sessions your site receives. A single-page session is when someone visits a page on your site and then leaves your site altogether, without interacting (clicking other links or reading more of your content) further with your site.
A high bounce rate can signal to Google that your visitors aren’t finding what they’re looking for on your site or that they don’t consider your site to be useful.
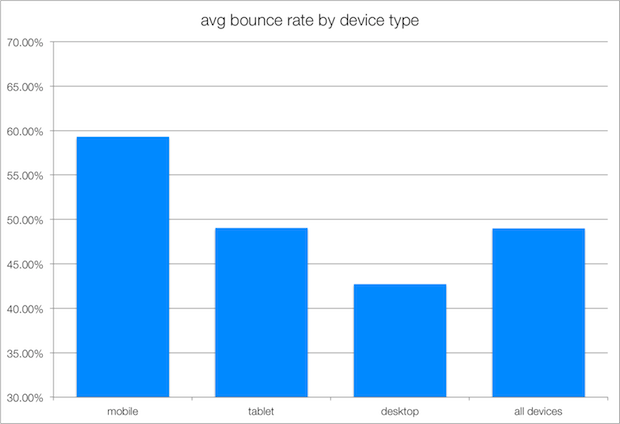
What’s an acceptable or average bounce rate?
The answer will vary depending on your industry. What truly matters when considering SEO power is that your conversion rates are increasing. Here is the average bounce rate by industry.
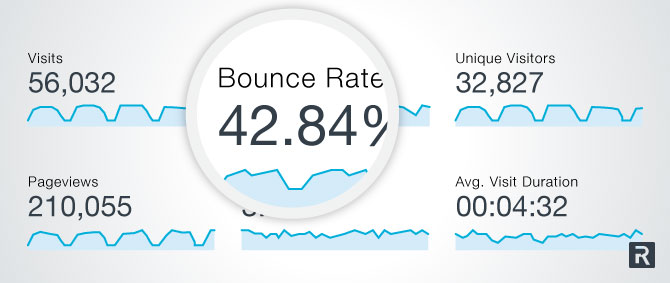
It’s absolutely possible to reduce your bounce rate and therefore reverse that trend. For instance, Recruiting.com reduced their bounce rate to 42.84%.
As a rule of thumb, if your bounce rate is above 60%, then you will probably want to work on reducing that number. The bounce rate below is fair. How does yours compare?
Site design and usability are the basic factors that affect your bounce rate. Remember, if users can’t easily find what they’re looking for on your page, Google as the website auditor assumes that your content is not useful. This is because the spider literally follows people.
When you engage your blog readers, they, in turn, engage with your site, which then lowers your bounce rate and gives your site a higher ranking score.
Bounce rates can fluctuate significantly over time and a bounce rate that jumps up a bit isn’t necessarily always a bad thing. It could be caused by a major tweak on your site. For example, when you redesign your blog, your bounce rate will likely increase a bit, temporarily, while visitors get accustomed to the new look and layout.
Speaking of design, don’t forget about mobile bounce rate.
Have you ever been to a site that looked like absolute trash on mobile? You couldn’t click anywhere, everything was way too zoomed in or zoomed out? When mobile visitors land on a page like that, all they want to do is click the “Back” button ASAP.
Over half of all search queries come via mobile devices. If you’re ignoring mobile site optimization you’re obviously turning potential traffic away.
You don’t want to be that site, do you?
Platforms such as WordPress boast responsive design themes which ensure that your site looks sleek across all devices. When in doubt, you can always run a mobile-friendly test to make sure that your site isn’t tuning out mobile traffic.
Low repeat site visits – If your site’s visitors only come to your site once and never to return, Google can take that fact to mean that your site isn’t all that relevant or useful. For some, being mobile friendly is a factor here too.
It’s a good idea to pay attention to your repeat visitor statistics as part of your rank tracker data. Once you’ve logged into your Google Analytics account, locate your repeat visitor statistics and then compare that number to previous months.
To adjust a low repeat visit number, reward visitors when they come back to your site after an initial visit. You can do this by offering a piece of useful content, such as a free valuable report or with gifts such as free access to an insider event or e-course. Additionally, look for ways that you can enhance the return-visit experience and satisfy your visitors who come back for more.
As an example, Amazon has one of the highest repeat visitor rates among shopping sites. When a visitor comes to Amazon the first time and looks at different products, Amazon will automatically track the user’s movements. When the visitor returns, Amazon serves up the same or similar products on all web pages.
Amazon also makes excellent use of an upsell strategy to persuade people to buy their products. This makes it easier for shoppers to find the exact product that they want to buy and encourages them to place their order instantly.
If your site doesn’t retain visitors and make them want to come back again, this could negatively impact your ranking.
In your Google Analytics account, you should also pay attention to the sources of your traffic. Many domains might be referring visitors to you, but some may be sending you more visitors who make return visits to your site.
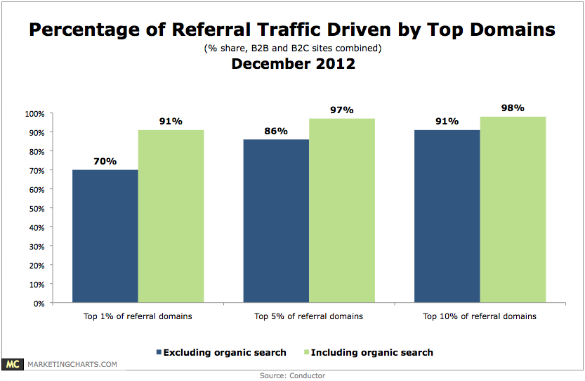
Focus on retention. Organic referral sources tend to be more reliable, in this regard, than social media sources.
Better Biz carried out a three-month study of both B2B and B2C websites to determine the best sources for targeted web traffic. Here’s what they found:
How can you get more repeat visitors to your site? Here are a few simple ideas that can help:
a). Decrease site load time – If you want to capture more repeat visitors, see if you can boost your site’s speed, especially if it’s on the slow side. According to Moz, “site speed actually affects search rankings.” Make your site load faster and your visitors will stay longer (and be more likely to come back in the future).
Although the direct impact on search rankings may not be terribly significant, as you’ll see below, it’s absolutely true that fast-loading sites create a better user experience and thus improve the perceived value of your site giving it more SEO power.
Here’s an interesting statistic: 40% of people abandon a website that takes more than 3 seconds to load. A slow-to-load page can result in a higher bounce rate, as well as a lower repeat visitors rate. This is especially true on mobile devices.
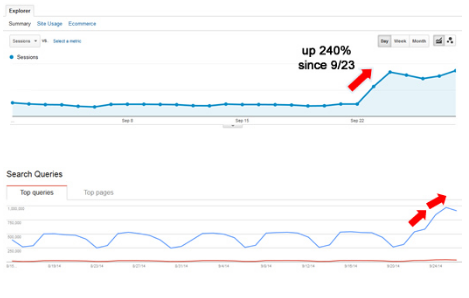
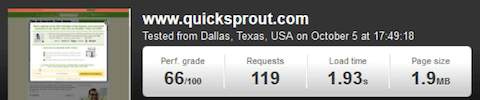
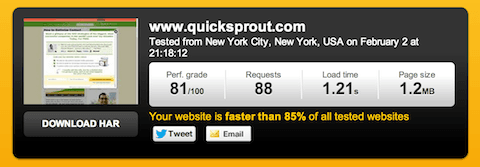
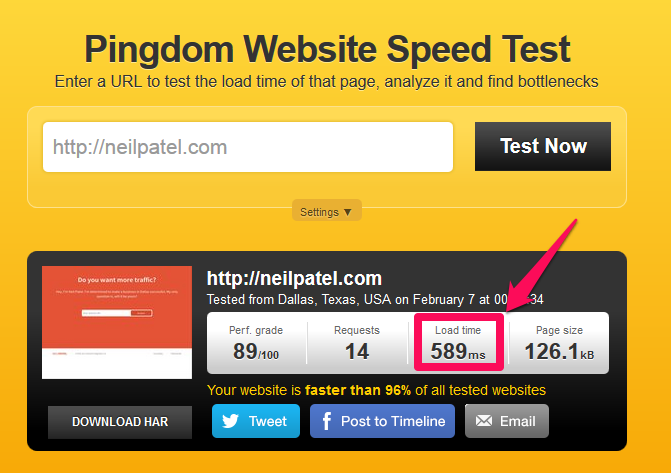
When I discovered that both Google and my readers love sites that load very fast, I plunged into the topic. My efforts resulted in taking my site from a load time of 1.9 to 1.21 seconds. In turn, this increased the direct traffic coming to my blog to 2,000+ per day.
Here’s my initial load time, before optimization:
And, here’s the result, after the guys at StudioPress reworked the code:
Again, considering that over half of web users expects sites to load within two seconds, you can’t screw around with load time.
Seemingly simple steps such as cutting back on massive homepage hero images can make all the difference. If you’re using WordPress, double-check for any clunky or outdated plug-ins which could potentially be slowing down your site.
Start improving your site load time today. You can follow this step-by-step guide.
b). Be Helpful – One of the five ways to get repeat visitors is to help people. Your content should be able to solve a definite problem. For example, you could write a step-by-step tutorial on any topic relevant to your site’s niche.
So, if you regularly write about SEO or internet marketing-related topics, you could provide a detailed Google Analytics tutorial guide, accompanied by explanatory screenshots. This guide would be a great example of targeted problem-solving content since a lot of people struggle to understand GA.
If you follow the rule of “be helpful” in regard to your content, you’re already way ahead of the game.
Really, though. Far too many marketers focus on fluff instead of actionable content that’s easy to read and quick to digest.
Ever wonder why in-depth “how-to’s” and long-form listicles currently dominate the blogosphere?
Because that’s what people want. Google knows this, and so should you.
And content creators are taking notice, too. The average blog post is longer than ever; meanwhile, writers are spending 25% more time on their posts today than they did last year.
This attention to detail makes all the difference for your audience and Google alike. In-depth round-up posts, such as this example detailed by Brian Lang of SmartBlogger, are a potential hotbed for traffic, shares and audience engagement:
This post didn’t drive over 4,000 social shares by accident. At nearly 8,000 words, such a piece was able to spread like wildfire because it answered a burning question for a hungry audience.
Ask yourself: how can you do the same on your site?
High percentage of boilerplate content – Boilerplate content refers to the content that you reuse on your site. For instance, a particular paragraph in a useful article might be reused in a few places on your site. One or two such paragraphs probably won’t do much harm. But, if the overall percentage of boilerplate content gets too high, your site could fall in a rank tracker.
As a general rule, avoid using the same or very similar content on more than one page on your site. Focus on unique content – that’s the best way to improve your rankings.
One kind of boilerplate that occurs frequently is “hidden content.” When you display a certain page to users and get other pages to be crawlable by Google, Google sees it as boilerplate content. Too much of that and your site could be penalized.
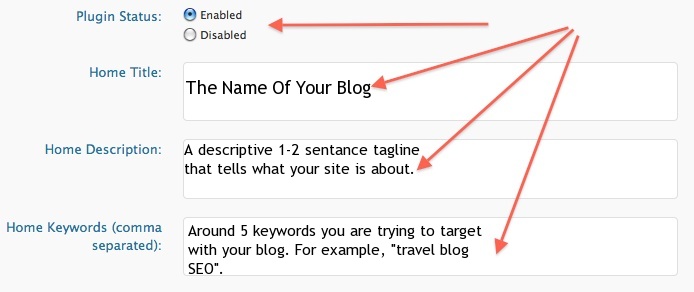
Irrelevant meta tags – It’s very important to set up meta tags precisely and accurately because irrelevant meta tags will increase your risk of getting a Google penalty by the website auditor. Here’s how to add relevant meta tags to your site’s pages.
Remember, meta tags consist of the title, the description, and the keywords.
If you’ve installed the All in One SEO plugin, you’ll find it’s easy to set up your meta tags within three minutes or less. Remember that Google Panda doesn’t like duplicate pages. Travel Blog Advice shows how simple it is to set up the plugin.
In the image below, you’ll see how Pat Flynn’s meta tags are specific and relevant to the page in question. However, in modern SEO practice, it’s not advisable to have a lot of keywords, even if they’re all relevant.
Note: Avoid excessive keyword placement, otherwise known as keyword stuffing. According to David Amerland, this can lead to a penalty for your site, when Panda updates are released.
How to Recover from the Google Panda Algorithm Update
How do you identify and recover your site from a Panda penalty? If your website or blog was hit by Panda, your next step is to figure out a plan to remedy the problem or problems. This can be difficult; there are many articles and blog posts online that discuss the theory behind the penalties but provide no actionable steps to take to fix the problem.
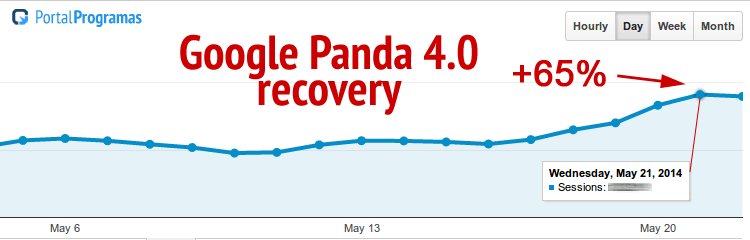
By taking action, Portal Programas recovered 65% of their web traffic after the Panda 4.0 update. And, they did it by following a simple plan that focused on user experience.
If you see a drop in organic traffic and rankings following a Panda update, you can be fairly sure you’ve been penalized by Google.
For Panda, you want to avoid showing people thin pieces of content on your site’s pages. Either beef up thin content or remove it from your site, especially on the archive pages that have 10 – 100 words.
Rewriting your content is another simple way to remove the penalty from your site, transforming it into a high-quality site in Google’s eyes. Eric Enge, Stone Temple Consulting President, told Search Engine Watch that one of his clients saw a 700% recovery by rewriting and adding content to their site.
Improve Panda Quality Score – In addition to removing thin content pages or adding more content to make them more detailed and helpful, you should also pay attention to your Panda quality score.
Follow this Panda quality equation to obtain a higher score:
- Static Elements
- Quality Checks
- User Experience
The equation above came from Google, so we can trust it to help us recover from a Panda penalty. Let’s explore each of the items:
1) Static Elements – Every site should have static elements or pages that state what the site does, who is behind it and any applicable terms of service. The static elements are usually: Privacy Policy, Contact, About and Terms of Service.
i). Privacy Policy – Most Privacy Policy content is regurgitated or generated with a third-party tool. You can always add a no-index or no-follow tag to this page’s <head> HTML element.
But, Google still prefers that you make this page unique. Avoid copying and pasting from other sources, as Google considers this to be duplicate content.
If you use a third-party tool, personalize and rewrite the content. After generating your privacy policy content, you can rewrite it. One good premium (paid) service to consider is MyPrivacyPolicy.
ii). Contact – Another static element on your site is the “contact” page. It’s usually thin, with less than 100 words of content but still considered by the website auditor.
It’s important you either no-index tag this page or add more content below the contact form or address, as Googlebots crawl and store home and office addresses, emails, authors, phone numbers, etc.
Note: Google has made it very clear that “if only one or two pages on your site are high quality, while the rest are considered low quality, then Google will determine that your site is low quality.”
Every page counts, so strive to make your static elements (contact page, About page, etc.) rich, unique and helpful.
iii). About – Your “About Page” is another important static element that can lift or lower your Panda quality score. Do you know How to Write the Perfect About Page?
Don’t overlook opportunities on-site to beef up your content. Even your “About” page represents a place to target keywords while also telling your story.
In a nutshell, you want to write unique and valuable content for this page, just as with all your site’s pages. Tell a story to captivate your audience and provide a clear call-to-action.
An “About” page with only a few sentences can lead Google to assume that your entire site is low quality. Take the opportunity to update your page – after all, it’s your story, your experience and your pains and gains.
iv). Terms of Service – Although most visitors won’t even click this page to read its content, it’s important you make it unique and Google-friendly. If you’re a blogger, adding this page to your blog is optional. However, if your site is an ecommerce or services company site, you’ll want to make sure that you have this covered.
The same rules that you followed when creating your “privacy policy” content also apply here. Try to craft a unique TOS page. Make sure it’s in-depth (700 – 1000 words) and, as far as possible, interesting to read.
2) Quality Checks – In the Panda Quality Equation we considered earlier, one of the factors that can help recover your site from a Panda penalty is a solid Quality Check. In other words, the site code needs to be excellent and should meet current standards.
Unmatched HTML tags, PHP errors, broken JavaScript and improper CSS rules can all result in a poor user experience. We know Google values a great user experience because it helps Google measure your site’s engagement.
If your site was built using older versions of HTML, you’ll want to consider upgrading the site using HTML5. Make sure that your meta description and title tags are unique and contain the relevant keywords that you’re targeting.
The Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress is a fantastic tool to make sure you’re crafting optimized content that reads well. Finding the balance between keyword density and readability, Yoast also ensures that you don’t leave out any crucial pieces of your SEO for each page on your site.
Although you don’t need to tick all of Yoast’s boxes, the plugin helps put you on the right path in terms of readability.
3) User Experience – Since Google Panda is a site-wide penalty that scores your entire site, you’ll want to focus on improving your site’s user experience. Remember: user experience is about users. When you improve your customer experience, you’ll recover from a Panda hit.
As you map user experience, check to make sure that all of these factors are addressed:
If your analysis shows a need to improve your site’s user experience, consider these questions to help get you started:
i) Do you provide any point of good user experience? If you sell a product or service, how do your visitors or prospects receive it?
ii) Does your content solve a particular problem? Your users will exhibit how satisfied they are with your site through their engagement with your content. Do they stay and read your content? Do they leave comments on your posts?
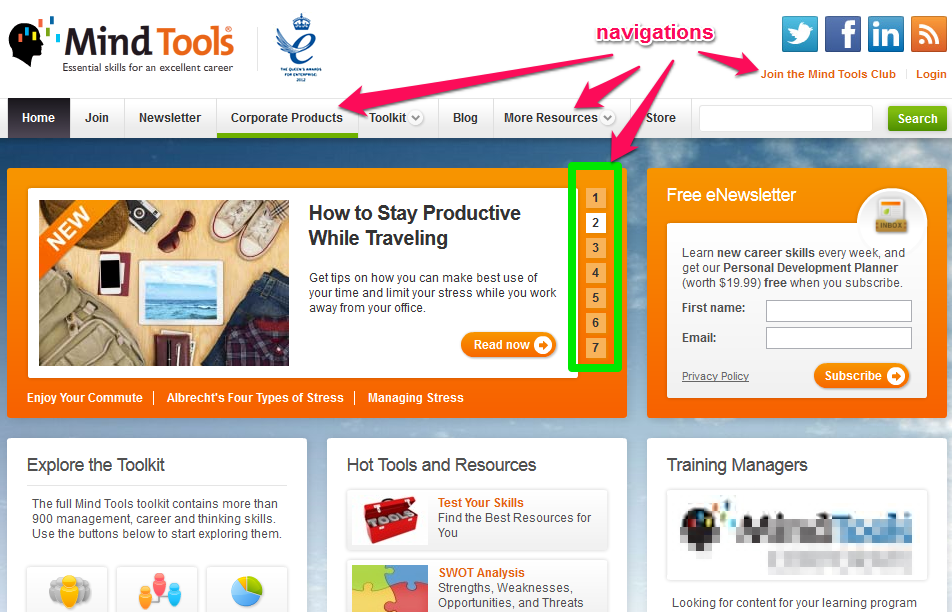
iii) Can you improve your navigation? If users can’t easily navigate from any part of your site to the homepage, you have some work to do to improve search results. Look for sites with excellent navigation – one good example is Mindtools.com.
The moment that your site’s navigation is enhanced, it’ll begin to improve your organic search results, rankings, and traffic. Make all your navigation links clickable and ensure that your search is working perfectly.
iv) Do users come back to visit your site? As we’ve already discussed, Google is concerned not only about your current visitors but also about your repeat visitors.
When your content is high quality, people will come back for more. If it’s not, then they’ll bounce, resulting in a low-quality SEO power score for your site and its web pages.
v). How quickly do your web pages load? If your site load time is less than 4 seconds, then you’re good to go. If not, then you have some room for improvement. Look for ways to make your site’s web pages load faster through optimization.
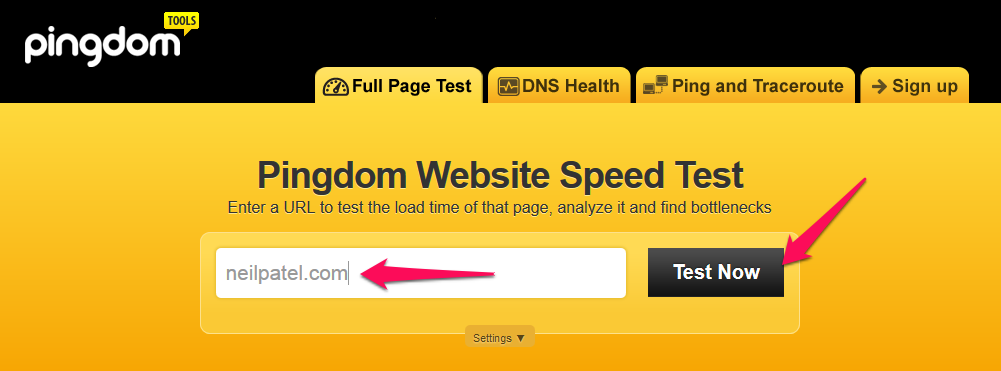
How do you find out the speed of your site?
Step #1: Go to tools.pingdom.com. Plug in your site URL and click the “Test Now” button.
Step #2: Check your site speed.
Some other common links between sites with excellent UX in mind include a simple yet attractive design, straightforward navigation, and crystal clear CTAs. Amazon is a prime (pun intended) example of such a site:
No, you’re not expected look exactly like Amazon; however, your site shouldn’t require visitors to dig for whatever they might be looking for.
Google Algorithm Update: Penguin
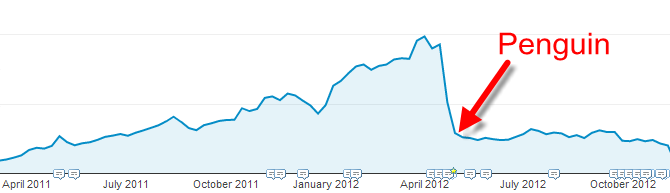
On April 24, 2012, Google released the first Penguin update. While the Panda update was primarily targeted at thin and low-quality content, Google Penguin is a set of algorithm updates that puts more focus on incoming links.
Before Penguin’s release, site owners, content marketers and webmasters all employed different tactics for link building.
A handful of those ways still work, but a majority of the old-fashioned link building strategies are dead. According to Rival IQ, there are four factors will get your site penalized by Penguin. See the image below:
i). Link schemes – Links are still important, but high-quality sites are the best way to improve search rankings.
Link schemes are those types of activities geared at generating links that will manipulate or induce search engines to rank your web pages. If you fall into the trap of always building links to your site from every other site found in search engines, you may be penalized by Penguin.
Rap Genius, a dedicated website that interprets lyrics and poetry, was penalized because Google found they were using link schemes to manipulate their rankings at the time.
Bottom line: Avoid all forms of link schemes. It’s just not worth the risk.
ii). Keyword stuffing – Matt Cutts already warned against stuffing your page with relevant keywords. No matter how in-depth and easy-to-navigate the site is, Penguin will most likely find and penalize it. In most cases, it’s easy to see why. This is especially true if you’ve ever actually seen a keyword-stuffed page. Here’s an example:
Buying Valentine’s gift for your spouse is a great step to take. This year, Valentine’s gift should be an avenue to express how much love you’ve for him or her. Make sure the Valentine’s gift is well-researched. But don’t stop there. Make it a culture to always show love to your spouse, whether there is Valentine celebration, Christmas etc. When you show love, you get love. For instance, when you show love today, you’ll live to be loved. Are you ready to choose the best Valentine’s gift?
Do you see how many times the keyword “Valentine’s gift” is mentioned in this thin piece of content? That’s keyword stuffing and it’s contrary to the Google Webmaster Guidelines.
Don’t use excessive keywords in your content. Don’t try to manipulate your rankings. If a particular keyword doesn’t sound good or doesn’t flow smoothly in the content, don’t use it.
Note: Keywords are still relevant in the post-Panda and post-Penguin era. Just keep your focus on the intent of your keywords, and write content that appeals to people’s emotions and solves their problems. Effective SEO has always been that way. Let’s keep it simple.
iii). Over-optimization – According to KISSmetrics, “SEO is awesome, but too much SEO can cause over-optimization.” If you over-optimize your anchor texts, for example, this could get you penalized by Penguin. The best approach is to incorporate social media marketing and gain natural or organic links to your web pages.
In April 2012, Google rolled out another update that penalized large sites that were over-optimizing keywords and anchor texts, engaging in link building schemes and pursuing other forms of link manipulation.
One of the signs that you might be over-optimizing is having keyword-rich anchor texts for internal links, i.e., anchor text that links to a page within your own web pages.
Here’s an example:
Learn more about Hp Pavilion 15 laptops and its features.
(Links to: example.com/hp-pavilion-15-laptops.htm)
Another example:
Do you know the best iPhone case that’s hand-crafted for you?
(Links to: example.com/best-iphone case-hand-crafted)
Note: When your anchor text links directly to a page with an exact destination URL, it can create good SEO. When it becomes too much, however, your site can be penalized for over-optimization.
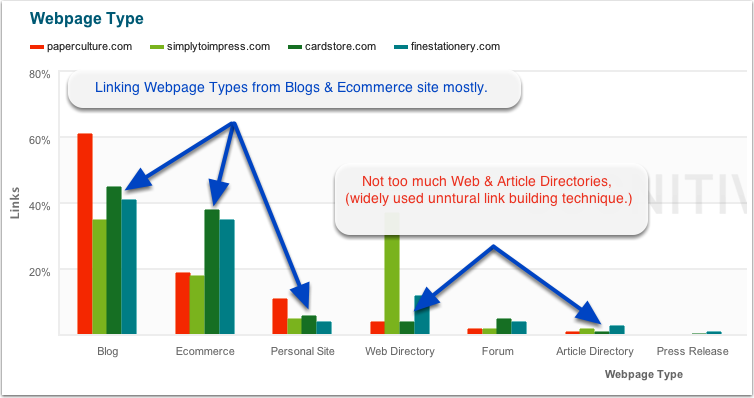
iv) Unnatural links – The funny thing about unnatural links is that they don’t look good to anyone – not to your readers and not to Google. These links may appear on sites that are totally off-topic. Cardstore lost their ranking through unnatural links that appeared in article directories.
Yes, such links worked in the past and larger sites were the best players of that game. Google Penguin destroyed the playing field for those big sites, which then lost all of the benefits of their hard work. The moral of the story: Your links should be natural.
When you buy or trade links with someone, there is every tendency that the anchor texts or links will be totally irrelevant. Here’s another object lesson: Overstock.com plummeted in rankings for product searches, when Google discovered that the site exchanged discounts for .EDU links.
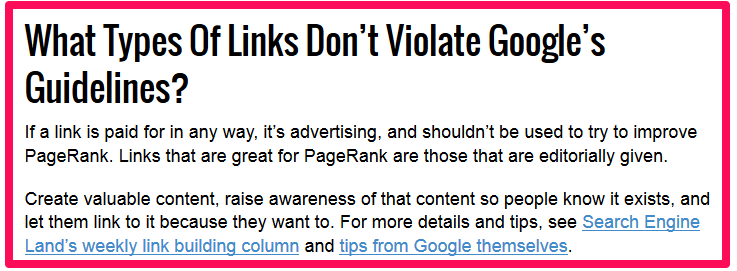
I don’t recommend link buying. But, if you must do it, make sure that the referring site is relevant and authoritative and that the links are natural. Here’s a better explanation from Search Engine Land:
How Penguin works – The Penguin algorithm is a search filter that depends on Google’s frequent algorithm updates and attempts to penalize link spam and unnatural links.
The Penguin code simply looks for aggressive link building practices aimed at manipulating the search engine rankings.
For example, if you’re building backlinks too fast for a new site, Google can easily detect that you’re aggressive and penalize your site or even delete it from their search index altogether.
Remember, any link that you build now or in the future with the intention of boosting your search engine rankings violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
Link exchanges, paid links and other forms of black-hat link building techniques are all bad SEO power practices. They may work for a time, but sooner or later, Google will find out. More importantly, avoid using link wheels or exchanges to manipulate search rankings.
How to Recover from the Google Penguin Algorithm Update
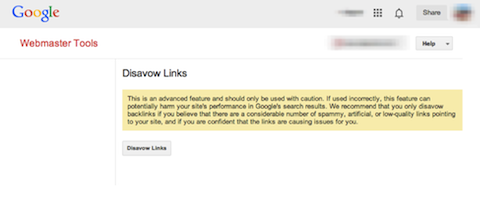
If you’re looking to recover from a Penguin hit, Google’s Disavow Tool is your best friend. This tool allows site owners to remove toxic and potentially spammy links manually.
Given the massive warning that Google provides with the tool, be sure not to disavow legitimate links to your site. This could end up doing major damage to your rankings.
Although link building is often associated with spamming, building legitimate links will make it possible for anyone to rank in Google’s search results.
If you want your site to attract legitimate links, you have to do the legwork to make it happen. There are tons of strategies out there for building backlinks which won’t result in a Penguin penalty.
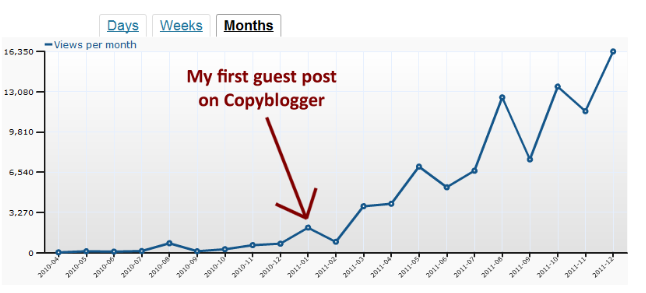
For example, guest posting on other blogs in your niche is the perfect way to point links back to your site. Doing so also aligns with the Panda update as you craft content relevant to you and someone else’s readers.
I attribute much of my traffic to guest posting and recommend that anyone in search of new visitors does the same.
Another great way to encourage links is to write posts which integrate influencers in your industry. Check out this example from Tor Refsland who generated massive traffic and shares by interviewing over eighty people in his niche.
These types of posts are a potential goldmine of traffic and links.
For starters, each of the featured influencers is likely to both share and link to the post thanks to being featured.
This kind of in-depth listicle goes hand-in-hand with the helpful content that the Panda update encourages.
Finally, let’s briefly address the issue of keyword stuffing.
Keeping yourself from keyword stuffing is simple when you follow this rule:
Write for people, not robots.
Want to fix up your old posts? No problem.
It’s more than possible to rewrite your keyword-stuffed posts in a more natural way. Beyond using plugins such as Yoast to keep yourself in check, also make a point to read your content aloud so that it sounds natural when spoken.
Don’t overthink the process of integrating keywords into your content. Be natural.
Check out how I integrated relevant keyword phrases into my SEO Copywriting Guide without coming off as pushy or spammy.
Once again, the specifics of the Penguin update boil down to user experience. Anything unnatural or spammy gets punished while those who produce legitimate content are rewarded.
The Correlation Between Google Algorithms: Panda vs. Penguin
When you pay attention to making your thin pages and low-quality content better, you’re building a site to which other people will naturally link. And, that’s the relationship between Panda and Penguin updates.
Even if your webpage contains unique, useful and in-depth content, the Panda update likes you but you’ll still face a Penguin penalty if your links are low-quality.
What’s the difference between Panda and Penguin? The Panda update is primarily concerned about quality content, while Penguin wants to drown spammy or aggressive links that strive to manipulate any search engine rank tracker.
It’s important to keep an eye on both updates. When your site is penalized by Panda, there’s a good chance that Penguin will affect your site, too. Some SEOs and site owners have experienced multiple penalties, all the while wondering what happened to their rankings.
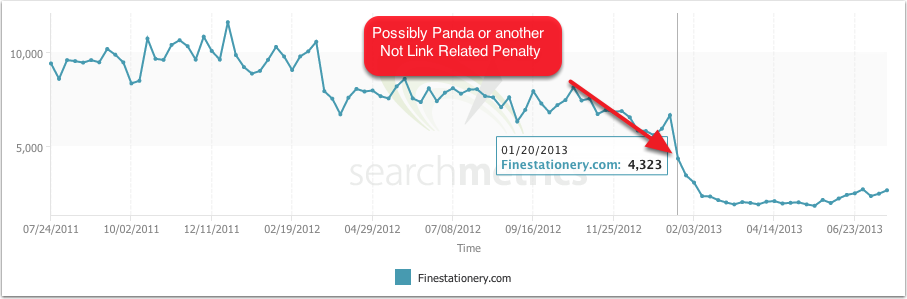
A good example of this interplay between Panda and Penguin is what happened to Finestationery.com. When the site began to drop in organic rankings, it wasn’t clear precisely what was happening. Was the site being penalized by Panda or Penguin?
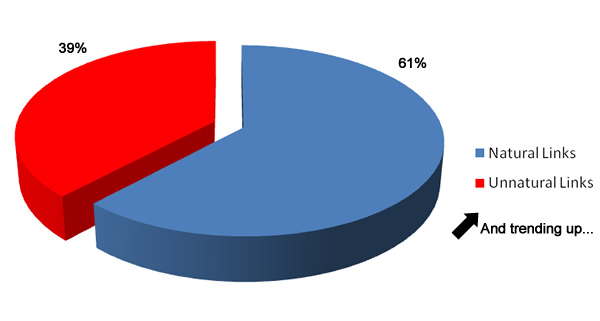
How to avoid a Penguin penalty – If you don’t want to get a Penguin penalty, then position your blog to earn natural links. Search Engine Watch shared an instructive case study of one site where they uncovered a mix of 61% natural links and 39% unnatural links and explained what steps they took to improve the site.
You can use Web of Trust (WOT) as a website auditor to gauge how much your visitors trust your site. If your WOT score is poor, then you have a bit more work to do, which still boils down to producing great content and building social engagement.
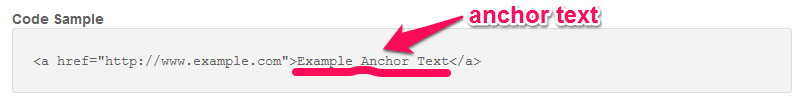
Understanding anchor text: Anchor text is simply the clickable text in your link. The hyperlink itself is masked or hidden. You can’t see the link’s destination URL until it’s clicked or hovered over, but the anchor text is visible on the page.
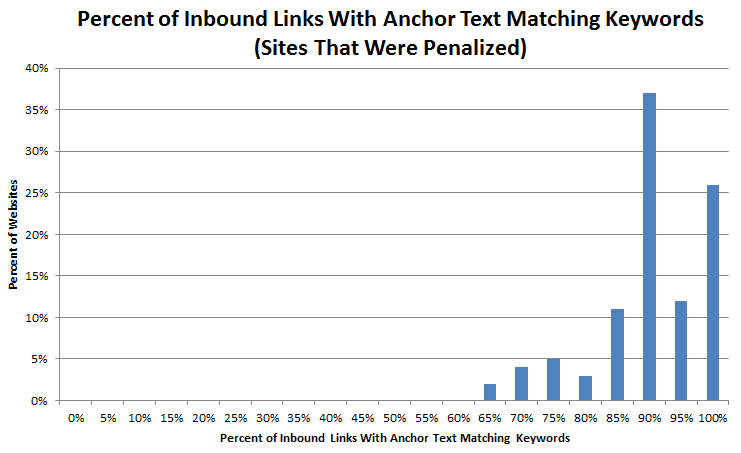
As it turns out, excessive use of exact keywords in your anchor texts can trigger a Penguin penalty. This was a stunning realization for many SEOs. For quite some time, SEOs had focused on creating anchor texts that precisely matched targeted keywords, in an effort to help build links.
After Penguin was released, many site owners experienced a huge drop in organic traffic and rankings. The reason is simple: excessive or “over”-use of precise keyword-matching anchor text.
Indeed, anchor text plays a vital role in the Penguin update. This is why it’s important to build the right kinds of links, using relevant and generic words, in order to reduce the risk of a Google penalty.
Other types of link and content manipulation targeted by the Penguin update can also get you penalized by Google:
Google Algorithm Update: Hummingbird
On September 26, 2013, Google released one of the most significant enhancements to the search engine algorithm to date. Hummingbird gives Google a “precise and fast” platform where search users can easily find what they’re looking for when they type a given keyword in the search engine.
Rather than treating two similar search queries like completely different entities, Google better understands “what” their users meant instead of what they strictly typed word-for-word.
In other words, this update is designed to improve its delivery of results for the specified keyword – and not just the exact keyword itself, but what we call the “keyword’s intent.” In a sense, Panda and Penguin were ongoing updates to the existing algorithm, whereas Hummingbird is a new algorithm.
This new algorithm makes use of over 200 ranking factors to determine the relevance and quality score of a particular site. Hummingbird serves as a sort of dividing line distinguishing the old SEO from the new.
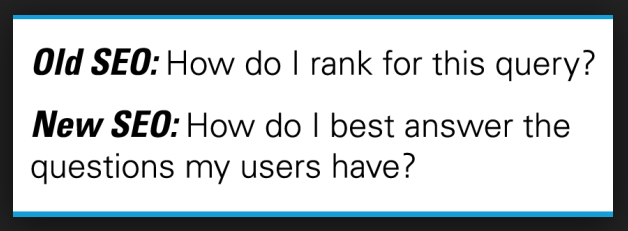
Now the focus is on the users, not the keywords. Of course, keyword research will continue to be relevant, especially when you want to explore a new market.
But, when it’s time to produce content that will truly solve problems for people, you should focus on answering questions. In today’s SEO, start with the user, execute with quality content and then measure the impact of your webpage links with a website auditor.
Jim Yu, CEO and founder of BrightEdge, explains some of the elements that still matter when you’re doing SEO in the Hummingbird era. Yu still believes that keyword research will continue to occupy the seat of power in SEO, but it should be done in service of the quality of your content.
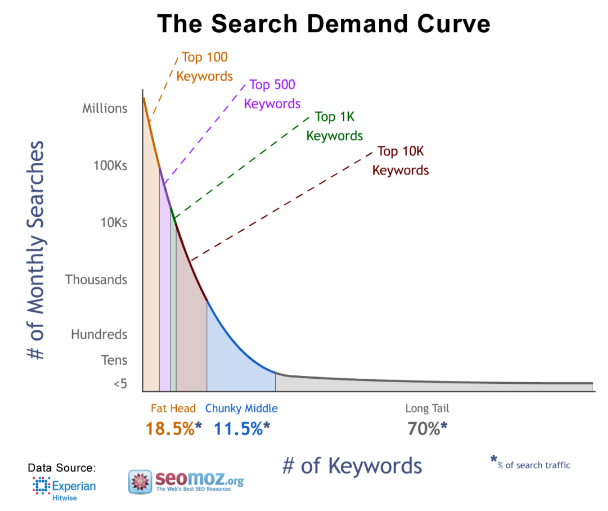
Note: Hummingbird uses long-tail key phrases, rather than seed/head keywords. Sites that use long-tail keywords have experienced a lot of success. 91% of my search traffic comes from long-tail keywords.
Marcus Sheridan has used and continues to use long-tail keywords to drive organic visitors to his River Pools Company Blog.
If you want to learn more details about Hummingbird and how it has affected SEO power since its 2013 release, the infographic from Search Engine Journal excerpted below will help:
Click Here To View the Full Infographic
Elements of Hummingbird: Since Hummingbird is not just an algorithm update, like Panda and Penguin, but rather a total change aimed at serving better search results to users, you should be aware of some of its more important elements. For all of these elements to come together and work properly, you must understand your audience.
How to Recover from a Google Hummingbird Update
Unlike the other updates mentioned so far, there aren’t really many specific fixes for Google Hummingbird. If your rankings are lacking, your best bet is to integrate more long-tail and conversational keywords while revising any of your previous, low-quality content.
Integrating long-tail keywords into your site represents a win-win situation for your site. For starters, long-tail phrases generate higher conversion rates versus simple single-word keyphrases. Highly targeted traffic is much more likely to take action versus those who stumble on your site by accident.
Secondly, consider that 70% of all search traffic comes as a result of long-tail keywords:
Whether you suspect you’ve been hit by a penalty or feel that your traffic has stagnated, there’s a good chance that you’re punching above your weight in terms of your keyword choice.
Think about it: it’s going to take a ton of content and links before you can hope to rank for a keyword phrase with thousands of searches per month. By focusing on long-tail keywords, you essentially build a foundation of traffic for your site which sets you up for more visitors and therefore more links over time.
For example, terms such as “coffee shop” or “Miami coffee” is beyond your reach right now. However, relevant long-tail terms such as “Miami cold brew coffee shop” or “best coffee shop in Miami” might be less competitive but totally relevant to your audience. This approach to keyword research and content creation goes hand in hand with the Hummingbird update.
Google now looks for sites to be relevant based on the scope of their content. If you’re using a variety of keywords and produce content that focuses on problem-solving, you’re probably on the right track.
Conversational Search and the Google Ranking Algorithm
Conversational search is the core element of Hummingbird’s algorithm change.
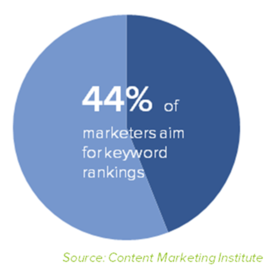
No matter what your niche may be, there are conversational keywords that will enable you to create highly valuable content. These days, people search the web in a conversational way. Forty-four percent of marketers aim for keyword rankings. But, there is more to SEO than keywords.
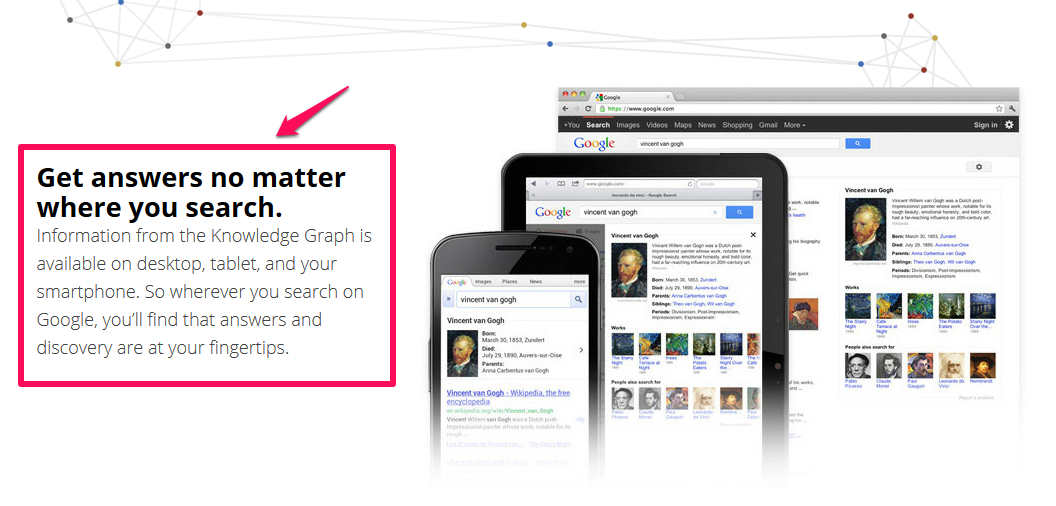
Google pulls data from their Knowledge Graph, along with social signals, to understand the meaning of words on a webpage.
Why is Quora such a popular site? There are probably many reasons, but it’s due in part to one simple fact: Quora offers experts from diverse fields who willingly answer questions in a conversational way.
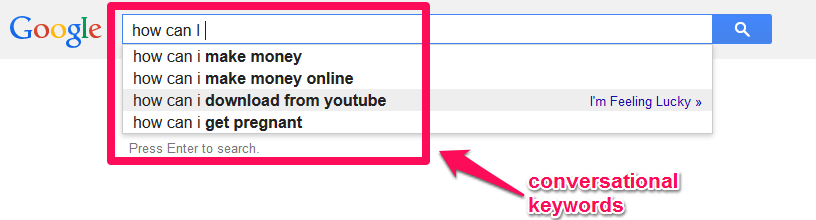
Site owners and content writers need to align their keywords and content, in order to best match the way people talk and search for information. Conversational keywords are question-based keywords. You’ll come across them when you carry out a search.
Your landing page should be able to answer the question that prompted the query in the first place. As an example, let’s say someone is searching for “best arthritis care in NJ.” Your content page should have that information for the searcher and not redirect them to an arthritis care site in Los Angeles.
So, how do you find conversational keywords or question-based & long-tail keywords?
Step #1: Launch Ubersuggest, Plugin a relevant “how to” keyword, and click “Search”
Step #2: Click “Keyword Ideas” in the Left Sidebar
Step #3: Identify your conversational long-tail keywords
With more than 500 keywords, there’s no shortage of choices. Some of my favorites from this list include:
- How to lose weight by fasting
- How to lose weight in a week
- How to lose weight in face
From the screenshot above, you can see that searchers are seeking information on several conversational keywords. They want answers from you. It’s your job to provide those answers in a conversational and, often, in a mobile-friendly, way.
“How to” key phrases and content, in particular, will better answer your users’ questions, which will prompt more engagement. In our example, you could write a weight-loss case study that’s useful, interactive and in-depth.
Around 87% of my blog posts are “how to” tutorials and that has been part of the reason for my success.
Remember: Post-Hummingbird, the users are the key focus.
Copyblogger also understands how to please their audience. Their blog post titles are magnetic and conversational in nature. Additionally, they understand their competitors, have a mobile responsive site and use social media to gain signals. All of these factors make Google delighted to send Copyblogger more traffic.
Speaking of mobile, also consider the search impact of “speech to text” platforms such as Siri which rely on long-tail terms.
Approximately 40% of smartphone users use speech to text regularly, which literally means that these searchers are having a conversation with Google.
As virtual assistants such as Siri evolve, conversational keywords will continue to dominate the SERPs.
Conversational search signals Google’s desire to reach their users on a personal level, ultimately improving user experience along the way.
Traditional advertisements tend to interrupt users, but useful and interesting content will lure them in and make them repeat customers. In other words, content is the new ad.
That’s the whole essence of content marketing – and it’s been my secret weapon for growing my software companies. You may not fully grasp Google’s policies, but follow Jenna Mills’ advice and your site will not only avoid Google penalties but will also enjoy improved organic rankings and traffic.
Google Algorithm Update: Pigeon
So far, we’ve talked about Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird and how these Google algorithm updates affect site owners who want to improve search engine rankings without getting penalized.
However, there are other algorithm updates and changes that have taken place since the 2011 release of the first Panda. Specifically, in July 2014, there was the Pigeon update.
I wrote an in-depth post about the Pigeon update here, but the specifics of the update are pretty straightforward.
Pigeon emphasized the experience of local searchers, which is crucial to meeting the needs of users looking for products and businesses on-the-go.
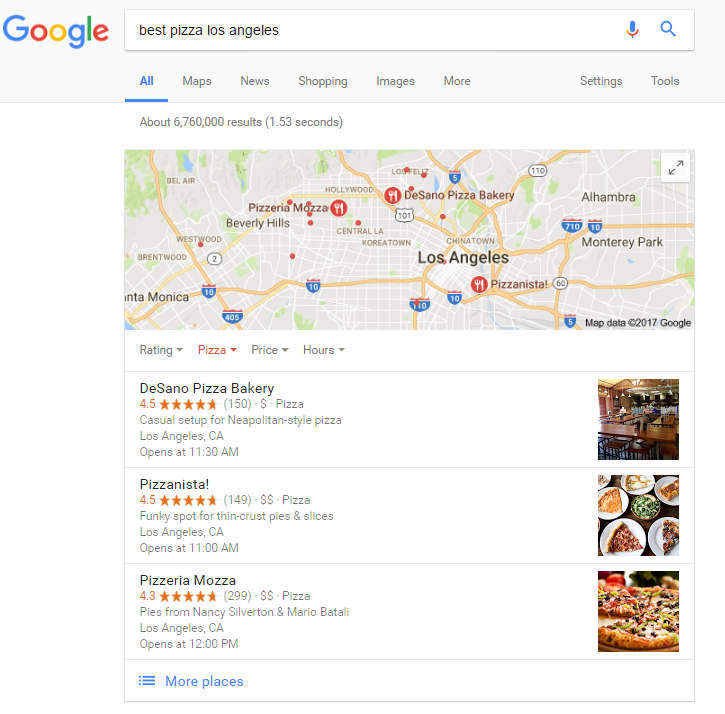
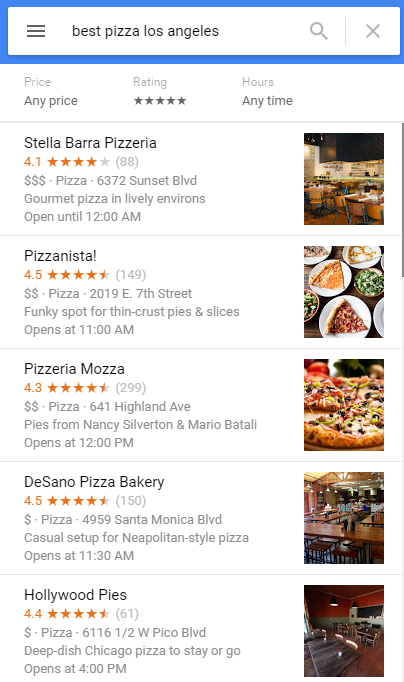
For starters, Google meshed the results of their search engine with Google Maps to produce the same results. For example, see what happens when you search “best pizza Los Angeles” in Google…
…and Google Maps
Similar results, right? As they should be.
Much like conversational search, Google took into consideration how synonyms play into local queries. If you search “best pizza in Los Angeles” and “where can I find Pizza in Los Angeles,” for example, the results are nearly identical.
Again, as they should be.
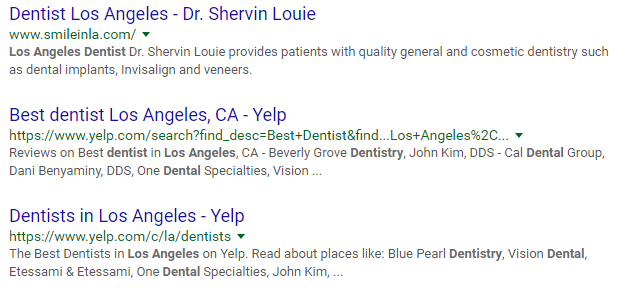
Pigeon also gave some weight to local search sites and directories such as Yelp, which had suffered via search in the past. If you search “Los Angeles dentist,” for example, the two of the top three results are from Yelp:
The update rewarded local businesses who integrate geo-specific keywords into their content. Pigeon also boosted Google’s ability for searchers to quickly find nearby businesses without having to search geo-specific terms themselves.
If you’re in Los Angeles looking for a coffee shop, you don’t need to specify your location to find a cup of coffee. “Coffee shop” is more than enough.
Seems like a subtle touch, doesn’t it?
But Pigeon is a great example of Google evolving their algorithm to better serve its users.
Google Algorithm Update: Fred
As of June 2017, there’s still a lot of question marks surrounding Google’s unconfirmed “Fred” update. According to Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Land, Google refuses to comment on the update. The update is suspected of targeting sites emphasizing revenue over quality content.
Schwartz surveyed over 100 different sites to determine the specifics of the Fred update. He noted that most of the sites impacted were sprinkled with affiliate links and provided little-to-no legitimate value with their content. Such sites saw traffic drops anywhere between 50 and 90 percent.
Many of the affected sites also wrapped their content around various ads, which comes off as spammy to Google and users alike.
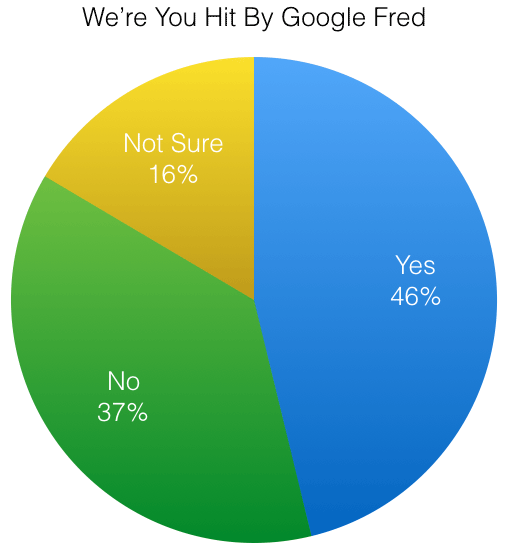
But just how many sites is Fred wreaking havoc on? A May 2017 poll by Search Engine Roundtable which surveyed 800 site-owners noted that a staggering 47% had indeed been blindsided by Fred:
If your traffic has taken a nosedive and you have no idea why, Fred could be to blame. Yet if we’ve learned anything from the history of Google’s algorithm updates, it’s that very few sites are beyond saving if you’re willing to make the appropriate tweaks.
Based on what we do know about the update, here are some changes to consider if you suspect that Fred is taking a toll on your rankings:
Rethink Your On-Site Ads
While blogging is a proven way to generate income, spamming your visitors with ads and affiliate links could be detrimental to your site. Not only do excessive ads potentially ruin the flow of your content, but also paint your site as a sales pitch versus an actual resource for your traffic. Avoid sneaky ad placement and instead strive to weave any paid links naturally into your content.
Audit Your Worst-Performing Content Pages
If you have particular pages that have tanked due to Fred, you need to assess the common content symptoms that those pages suffer from. To figure this out, you can audit your site to see what those low-performing pages are lacking.
Perhaps those pages are brimming with irrelevant keywords. Maybe they’re too short and don’t provide your visitors with actual value. Remember: Google loves long-form content and works against thin pages with nothing to offer.
You can’t afford to simply slap some words on a page and expect to rank anymore. In the era of Fred, those neglected pages could actually hurt you in the long-run. This is where plugins such as Yoast can be a potential game-changer as you understand at a glance what your pages are lacking in the eyes of Google.
Don’t Neglect Your Mobile Traffic
Google traditionally rewards sites that meet the needs of mobile traffic. Sites that do so today are no longer an exception to the rule as mobile traffic has surpassed desktop traffic. In other words, Google wants your site to be easy to navigate for mobile users.
Marketers should consider a “less is more” approach to their on-site design. Ditch unnecessary pop-ups and other bulky images that could potentially bog down your site. Focus instead on a mobile-friendly user experience that’s easy to navigate for those browsing via their fingertips.
Optimized navigation. Responsive design. Crystal clear calls-to-action.
If you’re sleeping on these pieces of your site, it’s time to wake up.
Recovering From Fred is All About User Experience
The common thread between these fixes for Fred is obvious: better user experience. While we don’t know everything about Fred quite yet, it’s clear that Google’s algorithm is taking steps to tackle spammy marketing tactics that were once commonplace.
Again, the initial impact of the Fred update yet again highlight’s Google’s crusade against low-quality content. This crusade ties directly back to Google’s ultimate goal of the best user experience they can possibly deliver.
Conclusion
I hope this Google Algorithm article has helped you to fully understand the major Google updates. These algorithm updates and changes have revolutionized SEO.
Google’s algorithms, from Panda to Fred and beyond, all work to help searchers find what they’re looking for while battling against low-quality content.
Through its algorithm changes, marketers understand what they can do to stay on Google’s good side. Additionally, we know what to needs to be done to fix our sites if something goes wrong.
So, let’s get down to the key takeaway from all of this.
You’re probably tired of hearing about the need to produce high-quality content, aren’t you?
Even so, Google’s algorithm history represents a blueprint for how marketers should approach their on-site content.
Helpful. In-depth. Original. You know the drill by now, right?
When you stay in Google’s good graces, you don’t have to work as hard. You also don’t have to worry about getting nailed with a penalty or watching your hard work go down the drain.
Don’t keep your site moving two steps forward and two steps back. By aligning yourself with Google’s goals, you’ll keep your site and its traffic moving in the right direction.
Bottom line: All you need to do is to build links in a scalable, organic way and focus on providing the best quality content (be it written blog posts or creative infographics) that you can, to grow your blog’s traffic.
What effects of these Google algorithm updates have you noticed on your site?




























Comments (352)