Imagine how baffled you’d be if you opened your Google Analytics dashboard tomorrow and found that your traffic had flatlined.
While this scenario is not common, it can happen if the search engine giant slaps your site with a penalty.
Everyone fears Google penalties.
I’m sure you do, too.
If you think that Google penalties only happen when Google changes its algorithm (like the Penguin update), you’re wrong.
Even now, as you read this, there might be a lot of sites that are facing some form of Google penalty even though there’s no major algorithm update.
Why?
Mostly because of following spammy practices, like buying links to boost one’s link profile, scraping content, offering poor quality content, stuffing keywords, and so on.
For example, do you remember the famous JC Penney Google penalty? When the search engine giant found that retailer JC Penney indulged in black hat SEO practices, like buying links, it took action against the site and, as a result, JC Penney lost its position on the top pages of the search engine’s results.
It was found that hundreds of sites were linking back to JC Penney’s site for thousands of highly targeted keywords. Mostly, the links were irrelevant and out of place as most of the backlinking sites had little to do with clothing.
This was a clear case of manipulating Google’s algorithm to grow their link profile and accelerate search results.
In another instance of a manual penalty, Google penalized a popular link network called MyBlogGuest.com.
As a result of the penalty, MyBlogGuest got wiped out from the organic results for their brand keywords. The ripples of this penalty were also faced by the sites that were involved in the link exchanges via that platform.
Not all penalties are a result of potential spammy practices. Sometimes, they might be due to negligence.
It could be because you didn’t monitor the backlinks to your site and so Google targeted your site due to the spammy links pointing to it. Staying on top of the health of your link profile is vital. A penalty could also happen as a result of negative search engine optimization, where your competitors target you.
Before we see the different ways of protecting your site from Google penalties, let’s first see the different types of penalties.
Types of Google penalties
Type #1: Manual penalties or SPAM actions
While most of Google’s penalties can be imposed in an automated way, there are some penalties that are imposed by the search engine giant’s human reviewers.
When a manual penalty hits your site, you’ll receive an alert in your Google Search Console dashboard.
You’ll also get an email alert.
Type #2: Algorithmic penalties
The algorithmic penalties happen when Google rolls out algorithm updates (like the Penguin update). And, this happens all the time. Since Google’s algorithms are running all the time, sites that violate Google’s guidelines keep getting penalized.
Algorithmic penalties are tricky to identify because unlike a manual penalty, you won’t get an email alert about it. The only way to know is to keep track of your traffic. If you notice that your traffic has dropped out of nowhere, it could be because of an algorithmic penalty.
Now, that you have a fair idea about how Google penalties happen, let’s look at a few ways to protect your site from them.
Monitor your link profile
Google looks at the following types of link-building/buying/exchanging practices as spammy:
- Buying and selling links
- Link exchanges
- Massive guest posting campaigns (targeting certain anchor texts)
- Article submissions
- (Excessive/spammy) Forum/comment posting
These link building campaigns generate unnatural looking links, something that Google bots identify easily. If your site is found to indulge in such black hat link building practices, the search engine giant will surely penalize you. For link building, they want to see you earning one natural link after another, not the practices outlined above.
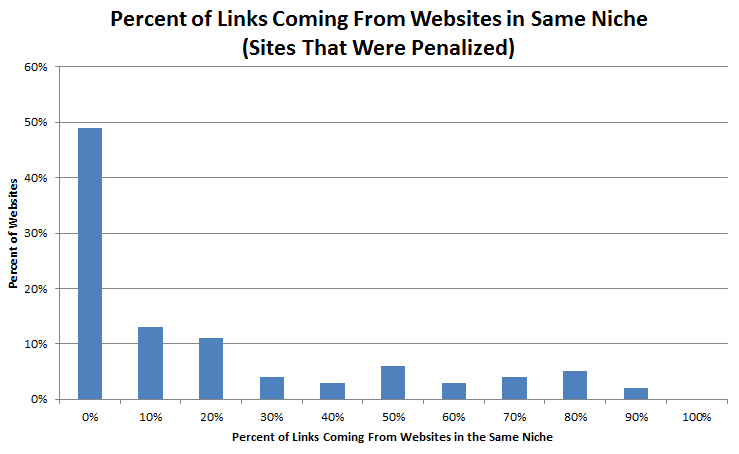
Other than the above, it’s also important that the sites that link to your site are also ideally from your niche.
For example, if you run a custom jewelry store, you can’t have dog store sites linking back to you. This sends a signal to the search engine giant that something fishy is going on.
The JC Penney Google penalty case that I mentioned above is a classic example of unnatural links where sites that had nothing do with clothing linked back to the Penney’s site.
Expedia, an online travel agency, lost 25% in search visibility when it faced a Google penalty over purchased links.
It was reportedly involved in buying links that had little to do with their product or relevant verticals. Apparently, Expedia’s case was a clear attempt at manipulating the search engines.
Link building is indeed your most important offsite search engine optimization activity. You have to focus on link building to build your site authority, to improve its SEO and to drive traffic to it. However, look for organic ways to get backlinks.
Create content that other sites love to link back to and that people on social media will be stoked to share. Quality content is the single most effective means of building a rich link network.
If you’re afraid that your site has unnatural backlinks, find and fix them.
Fight Negative SEO
Your competitors can hurt your search engine optimization efforts and can even get you penalized by Google by doing negative SEO on your site. The most common practice in negative SEO is to get a lot of spammy sites to link to you.
If Google finds spammy sites linking to you, it might think of your site as low-quality. This also affects where you rank with the search engine giant (and others) and increases your risk for a penalty.
So, if you notice spammy sites linking to you, disavow those links. Create a simple text file with all the spammy incoming links and then upload it using the Google disavow links tool page.
Fighting negative SEO is a required step to protect your site from Google penalties.
Offer rich, useful, and unique content
Google considers the following types of content as poor or thin content:
- Automatically generated content
- Thin affiliate pages
- Content from other sources. For example: Scraped content or low-quality guest blog posts
- Doorway pages
If you offer any of these on your site, you might be subject to a Google penalty.
Also, while Google doesn’t have a penalty for duplicate content, it expects sites to offer unique content.
Don’t target specific anchor texts
Anchor texts are the words or phrases that you use to link to a site. Since a link’s anchor text is an important metric that tells Google about a link, black hat SEOs started abusing it to target specific keywords.
To handle such anchor text spamming, Google detects and penalizes fishy instances of anchor text hyper-targeting.
Links with optimized anchor text in articles or press releases distributed on other sites. For example:
There are many wedding rings on the market. If you want to have a wedding, you will have to pick the best ring. You will also need to buy flowers and a wedding dress.
Brian Dean from Backlinko also stresses on this malpractice. He suggests:
Get Smart About Anchor Text: Use branded, domain, and webmaster name anchor text more often.
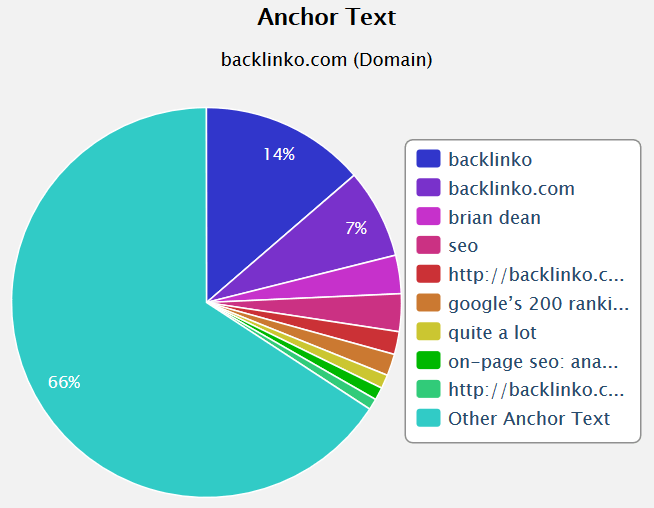
For backlinking to his own site, Brian uses a nice mix of anchor texts:
- Branded: Backlinko (14%)
- Domain: Backlinko.com (17%)
- Webmaster name: Brian Dean
Further, Moz suggests that 17% of your anchor texts should be your brand terms.
Since SEO is a core brand ingredient, it makes sense to consciously use branded anchor texts. This won’t just help you rank for your brand keywords, but will also help you gain higher exposure for your brand.
But, again, don’t overdo this or Google might smell something fishy.
Guest post cautiously
Guest posting isn’t dead — it’s a great link building strategy that can strengthen your site’s SEO as well as to get traffic to it.
However, guest post cautiously. That is, choose relevant guest post targets and use meaningful, natural anchor texts.
Also, when you try to build your link profile, don’t aim for too many backlinks in a very short time. Such rapid link building could be seen by Google as unnatural and could trigger a penalty.
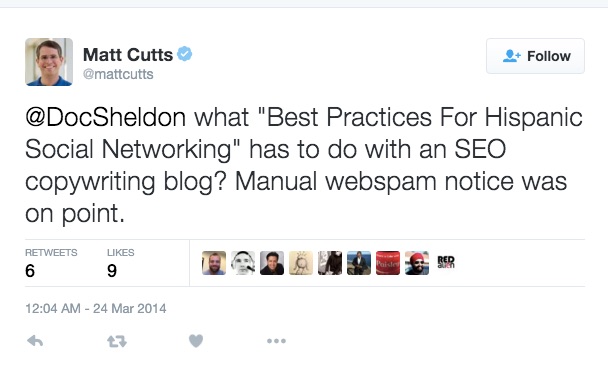
When Google penalized SEO Doc Sheldon’s entire site for a single guest post, he wrote an open letter criticizing the manual penalty. Google penalized his site for using a keyword-rich anchor text “hispanic data” used for linking back from the guest post.
Here’s Matt Cutt’s tweet explaining the penalty:
You might find it unfair, but the fact is that you can’t ignore Google. When guest posting, choose correct, natural phrases for linking back to your site. If you use anchor text that sounds too vague or disconnected with your site niche, the search engine giant might penalize you.
Don’t make users scroll too much for content
With its “Page Layout” algorithm, Google made clear that it expected sites to offer relevant content immediately to the users.
About the Page Layout algorithm, Google stated:
We’ve heard complaints from users that if they click on a result and it’s difficult to find the actual content, they aren’t happy with the experience. Rather than scrolling down the page past a slew of ads, users want to see content right away.
Google will penalize your site if you show a lot of ads within its above-the-fold area.
If your site’s fold area is full of ads – consider redesigning it to move content to the top. By doing so, you’ll be able to offer content immediately and without requiring your users to scroll a lot to reach it.
Watch your site for hacking
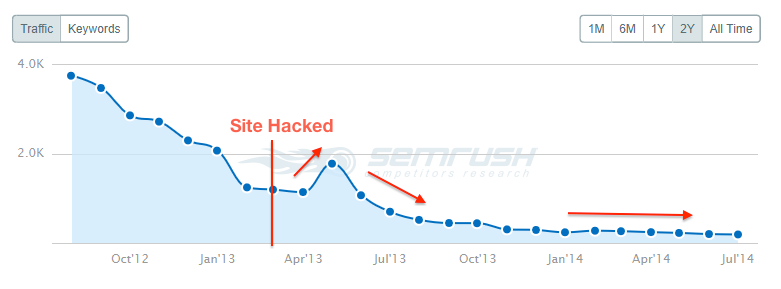
Your site can face a Google penalty if it gets hacked. There are lots of examples of sites getting penalized as a result of hacking.
An online university called Christian Leadership University Online got penalized by Google when it got hacked. Hackers created many spammy backlinks to the site and thus triggered the Google penalty. Of the 5,054 links examined, 600 turned out to be spammy.
As a result of the manual penalty, CLU’s traffic dropped dramatically:
It was only after CLU started the manual action removal process that the penalty got revoked.
In another case, a site got completely wiped out of Google’s index because of getting hacked. In this case, the hackers employed cloaking methods and made the site face a manual Google penalty. While the owner removed the malicious code within hours of the breach, the site still got penalized.
What’s noteworthy about this is that Google could find and flag (and penalize) the site, although the malicious code lived on the site for only about 3 hours. Google did revoke the manual penalty, but we all know there’s no instant fix to a Google penalty!
Getting hacked is the worst reason for facing Google penalties because it truly isn’t your fault. The best solution is to better protect your site to avoid such penalties.
Remove user-generated SPAM
It’s true that user-generated content can be your most valuable content. However, the same content can cause you a Google penalty if it’s spammy.
Google penalized Mozilla when it found spammy user-generated content on Mozilla’s site.
In its penalty alert, Google wrote:
Google has detected user-generated spam on your site. Typically, this kind of spam is found on forum pages, guestbook pages or in user profiles. As a result, Google has applied a manual spam action to your site.
To reasonably protect your site from a penalty due to user-generated content, use the “nofollow” tag. The nofollow tag will tell the search engines that you don’t endorse any of the links in the user-generated section.
Submitting request for reconsideration
Google recommends sending reconsideration requests, in the case of manual penalties. You can find the step-by-step instructions to recover from a Google penalty here.
If you realize that your site has faced an algorithmic penalty, you should work on the problematic areas and be patient. As algorithms keep updating, your site will be re-evaluated and then it could regain its position and traffic, once the penalty is revoked.
Conclusion
I’ll admit that facing a Google penalty can feel scary, but you don’t have to live in fear of Google penalties.
The search engine giant only goes after sites that try to manipulate their search engine rankings. Build your link profile with honest best practices and your vulnerability to receiving a penalty will decrease.
Unless you indulge in black hat SEO or ignore the simple suggestions I’ve made in this article, it’s very unlikely that you’ll face any Google penalty.
Besides, if you do, you can always sort the issues and request that Google reevaluate your site.
Have you ever faced a Google penalty? And how do you stay safe from them? Please share in the comments below.

Comments (82)