It seems like every other week we see the following headline:
SEO is finished! SEO is dead.
I’ve read a few of those articles in the past few weeks alone and countless times over the past few years.
But why? What’s causing people to think that SEO is dead?
Well, one reason is the fact that Google changes their algorithms 500 to 600 times every single year.
That’s almost two times per day. It’s nearly impossible now to keep up with Google’s constantly-changing ranking factors.
One day it’s all about links and the next thing we know, it’s social presence.
Trying to optimize your site for search engines in 2017 is one of the most confusing tasks you can give someone.
Do you optimize meta descriptions? Do they even matter anymore? What keywords should you use? Do those make any difference?
And in 2015, Google dropped yet another bombshell on us:
Google was making huge investments in machine learning and artificial intelligence to filter search results and rankings.
Awesome — yet another factor we have to take into account when trying to build our organic presence!
Google called this new AI implementation “RankBrain.” In 2015, they officially told us that AI technology would help determine search results.
They even placed heavy importance on the ranking aspect of the new technology and how it would impact search placings.
In this article, I’ll give you the 4-1-1 on what RankBrain is, how it works, why you should care, and how you can optimize your search results for RankBrain.
What is RankBrain?
Google search results have changed dramatically over the past few years.
From rich snippets and cards to the knowledge graph, the search engine keeps getting better and better:
The entire goal of Google is pretty simple: To give the user the best search engine experience in the least amount of time.
That means that when you search for a query, you are going to get nearly instant results:
Google is all about giving us the information that we seek. There are no ifs, ands, or buts about it.
But Google doesn’t work the same way that it used to.
For example, when you used to search for a keyword, you’d bring up millions of results for pages that used that keyword in their text.
So in those days, how would you take advantage of this for SEO? You’d plug that keyword into your content over and over to trick Google into showing your content.
We now commonly refer to this tactic as “keyword stuffing,” and it used to look like this:
And it was one of the best ways to rank your content.
Google’s search engine wanted to show the content because it seemed relevant.
But now, Google search results are vastly different. Google doesn’t just read your content and rank your website for keywords.
They look at context now, which means that they can tell by your search terminology what you really want to see.
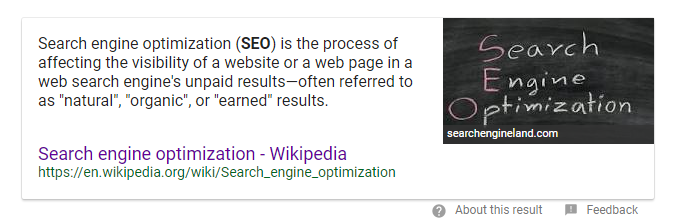
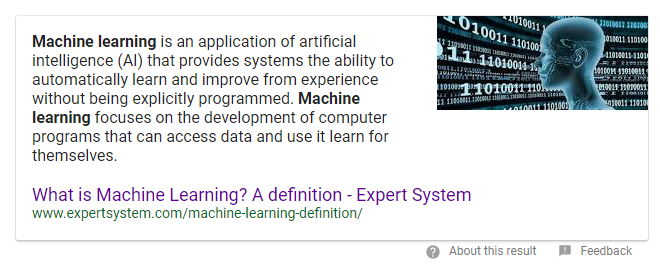
For example, check out the results for my search on SEO:
They showed me a definition in the form of a rich snippet.
Why didn’t they show me a website spamming the word SEO over and over again? It’s because machine learning interpreted my search query in a specific way.
Think about it: If you’re searching for a keyword like SEO, why are you searching for it?
You’re clearly not searching for SEO services. And you’re not searching for SEO tactics. If you were, you would have typed that.
You are most likely searching for the definition to learn what SEO is.
And Google started to understand this and provide the most reasonable result for that search type.
Google is now essentially capable of understanding and recognizing how words shape context.
And RankBrain is a tool that furthers this understanding.
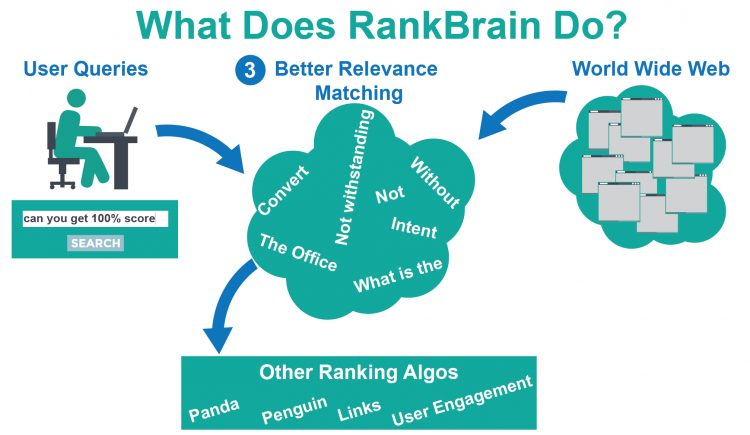
So, what exactly is RankBrain?
RankBrain is a machine learning system that uses artificial intelligence to improve search results and interpret new queries.
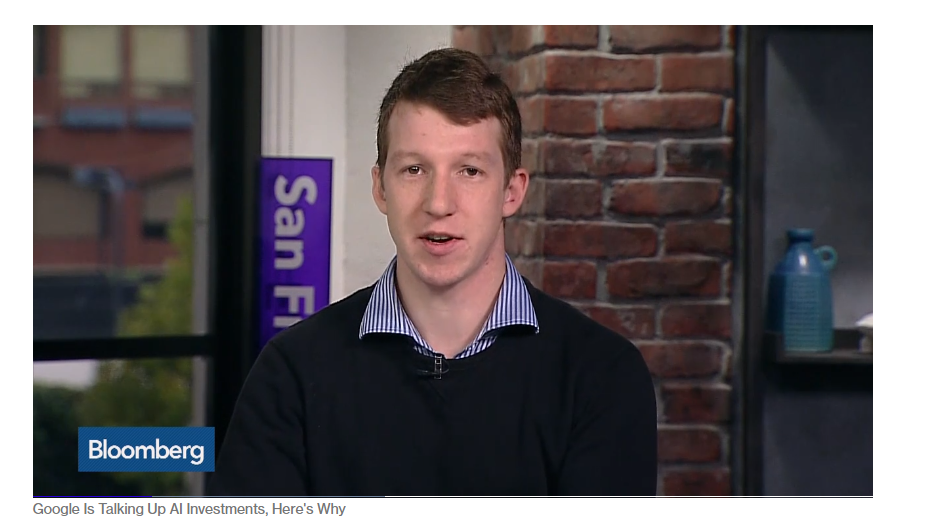
Bloomberg released the first statement about RankBrain from a senior research scientist at Google named Greg Corrado.
If you watch that video, you may notice one of the most important phrases that Greg used to describe RankBrain:
“That phrase seems like something I’ve seen in the past, so I’m going to assume that you meant this.”
Essentially, the RankBrain system takes difficult or hard-to-understand queries and relates them to previous searches based on intent and end results.
Google RankBrain helps to sort out searches that Google has never seen before and relate them to existing searches:
The system helps to identify patterns behind search keywords that are generally difficult to understand by connecting them to other search queries.
This means that Google can still provide the most accurate results for brand new search terms.
They do this to keep users satisfied and to serve up results that searchers want no matter how long or different the search term is.
Now that you know a bit more about RankBrain, let’s take a look at a real example.
RankBrain in practice
Google hasn’t given us many specific examples or instances where RankBrain has helped our search results.
But in the original Bloomberg release article, they gave us one example:
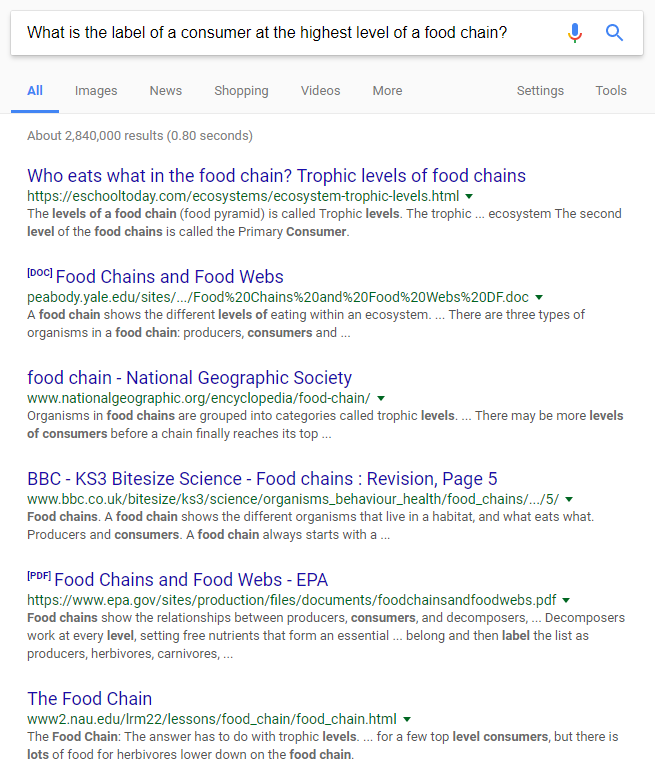
What is the label of a consumer at the highest level of a food chain?
If you’re like me, you’re probably wondering what the heck this search even means.
It’s a prime example of real searches on Google. I’ve been there before too, searching with a query that truly doesn’t make sense.
Take a look at the results for this query, though:
That’s pretty interesting if you ask me. RankBrain does a good job of connecting multiple aspects of that search to results from other similar searches.
RankBrain took a somewhat complex search query and turned it into fantastic results.
With that search, the user was likely trying to find information about where a consumer fits in the typical food chain.
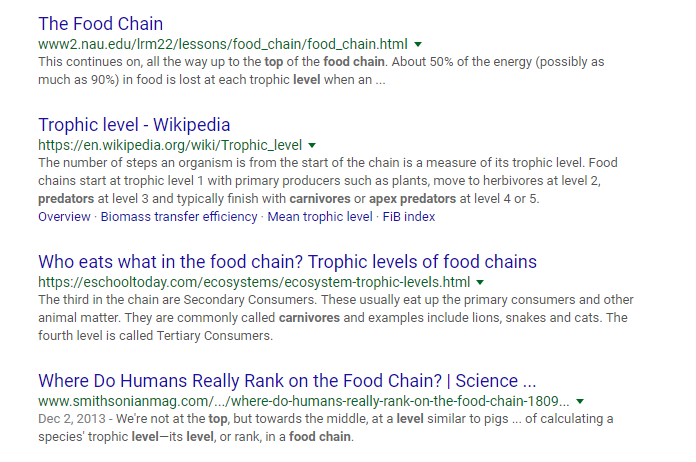
Now look at the search results for “top-level food chain” that could be comparable to the intent of the example above:
Almost identical results, right?
That shows that Google’s RankBrain is taking that complicated, diverse search query and picking it apart.
They are taking specific cues from the search and connecting it to popular searches like “top-level food chain” to give better results.
Check out this visual example on how RankBrain takes specific parts of queries to connect them to other ones:
In that search above, it’s pretty difficult to gather what the searcher really wanted to see.
Did they want to see what level a consumer is on the food chain? Did they want to learn about consumers at chain food stores?
RankBrain works by taking segments of the entire search and relating them to the most popular searches with those related terms.
What are machine learning and artificial intelligence?
To really get a firm understanding of what RankBrain is, we need to learn about machine learning and artificial intelligence.
These both play a significant role in how RankBrain works and how Google will continue to function.
Let’s get started with machine learning first.
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence that helps existing computer systems automatically learn and improve the user experience without being told what to do.
Machine learning takes user behavior and uses it to understand what works and what doesn’t.
By using frequent patterns and behaviors, machines can predict and deliver content based on common history.
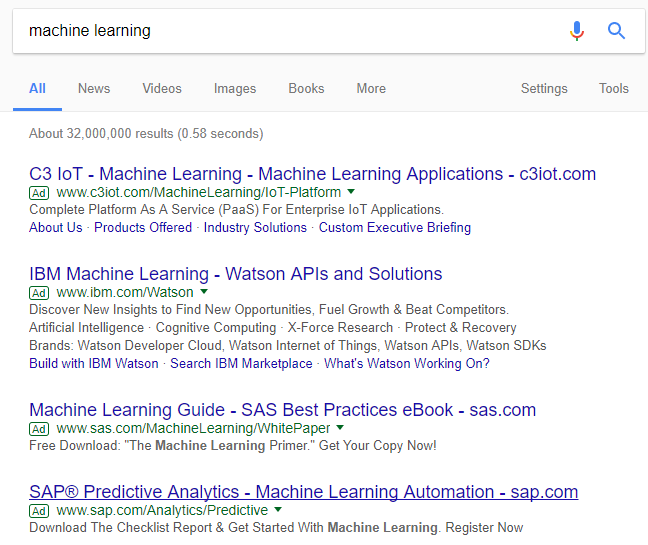
For example, let’s say I search for “machine learning” on Google, but I don’t get what I’m looking for:
Because the results aren’t there, I need to modify my original search query.
This time, I search for “what is machine learning:”
Great! That result is 10x better than the previous results.
And Google’s machine learning capabilities will start to pick up on that.
They learn that my original search led me to rephrase it to find the result I was looking for.
By not clicking on any results for the first search, the machine understands that the query wasn’t delivering the right results.
But when I rephrased my search results, I found the content I was looking for.
That means that Google can correlate those searches in the future. They can make content that shows up for “what is machine learning” also rank for “machine learning.”
So why is machine learning important?
Machine learning is a massive factor in how search engines display results. If your content doesn’t match up to the user experience, you can kiss your rankings goodbye.
Machine learning seeks to provide the best user experience by learning context and delivering content that makes sense.
So if you’re gaming the system, Google will learn that your content isn’t being clicked on for searches.
With that in mind, you need to focus on optimizing content for real people and learning the context behind a search.
The intent behind searches is what will drive rankings. If someone searches for “SEO” and you try to sell them services, you won’t rank.
If you explain in detail the history and definitions of SEO, you will.
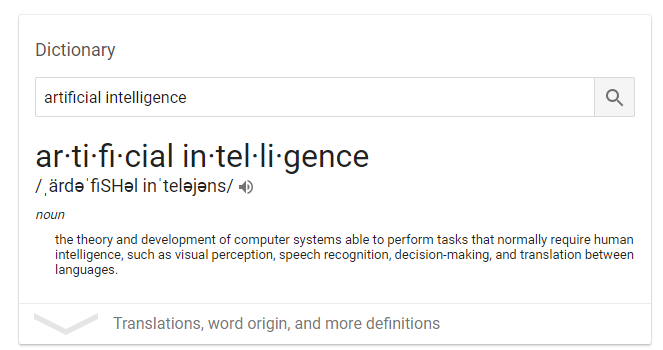
So what is artificial intelligence? Here’s what Google has to say:
Artificial intelligence seeks to help computers understand and react like humans when they get specific tasks.
This ties into RankBrain because the system seeks to understand how real users interact with Google and how they can make snap decisions based on translation and recognition.
It’s pretty amazing, right?
Machine learning and AI are big components of Google’s future and are already playing a role in RankBrain.
Here’s why you need to care about RankBrain.
RankBrain is the third most important ranking signal
In 2015, Senior Google Analyst Greg Corrado went on Bloomberg to discuss the announcement of RankBrain.
One particular statement that he provided gave us insight into how it would impact rankings in organic results.
He essentially said that RankBrain is one of the hundreds of things Google uses to determine search engine results.
That means it’s a big factor in organic rankings.
But here’s the difference:
The hundreds of other ranking factors come straight from Google engineers and their experiments.
RankBrain, on the other hand, is machine learning and AI technology that independently learns from queries to give results.
Greg Corrado also told us the following:
“It is the third most important signal in the search engine.”
That makes it a top factor when it comes to showing your content in organic results.
If you simply ignore RankBrain and the technology behind it, you’re risking your organic rankings and traffic from organic search.
So, what are the two other ranking factors that make up the big three?
They’re your content and links.
In 2016, Search Engine Land conducted a Q&A with Andrey Lipattsev, a Search Quality Senior Strategist at Google, in which he stated that content and links were the top two ranking factors.
He also repeated Greg’s statement in saying that RankBrain is the third.
According to SEL, there are dozens of ranking factors:
But the top three are content, links, and RankBrain.
So you can’t afford to ignore RankBrain. You have to care about it if you care about organic traffic.
Google uses RankBrain in every search and it impacts rankings
In 2015, just 15% of Google searches fully utilized RankBrain.
It hardly filtered any searches that users conducted.
But in 2016, Google told us that their confidence in RankBrain was steadily increasing.
And now, RankBrain and machine-learning tools are handling every single search query.
Massive amounts of search queries will have different results than they once did.
Different results mean different rankings and impacts on organic traffic.
In 2016, Steven Levy broke a story that had incredible data on how RankBrain really was impacting search results.
Here’s the main quote that stood out to me:
RankBrain is “involved in every query.” It impacts rankings “probably not in every query but in a lot of queries.”
This is difficult news for any marketer or SEO to hear. They aren’t being very definitive when it comes to our livelihood.
Does it impact our search traffic? Do we need to optimize for it? What in the world does it actually do?
All we can do is trust that Google is telling us the truth and that RankBrain really is impacting search query rankings.
And when you look at the data, it makes sense. Here’s a visual depiction of RankBrain in action:
It takes a user’s search query and matches it by relevance to other queries, giving results based on those similarities.
And considering that Google now uses it in every single search, we know that rankings will shift.
As machine learning understands behavior, it can tell if results are correct or not.
Remember that example I gave earlier?
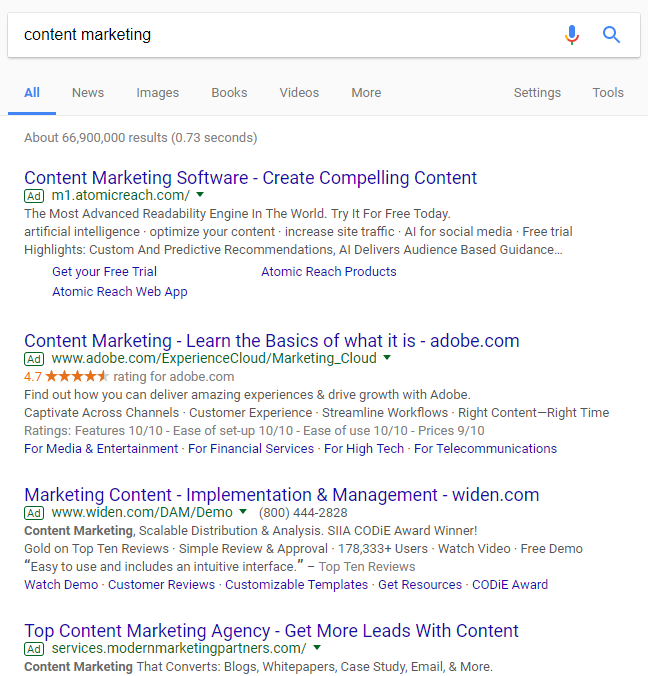
Let’s say that you search for something like “content marketing” and you only get ads or agency results:
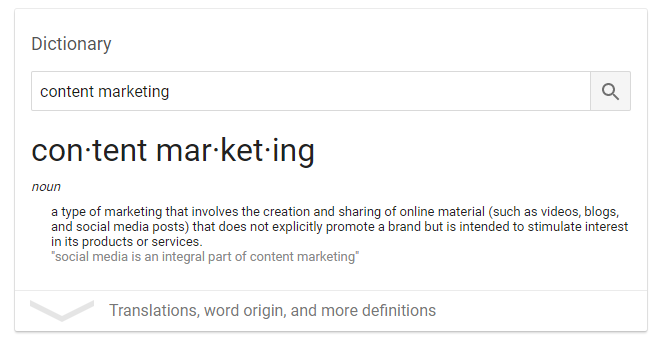
But you don’t click on any of these results. Instead, you modify your query to “what is content marketing” to get this result:
RankBrain will learn that you had to modify a search query to get the result.
If enough people are doing this modification to find better results, they will adjust the content that it shows for that specific keyword.
So, instead of showing ads and agencies, RankBrain will show you definitions and articles explaining content marketing.
All of this data leads us back to one simple point:
Google is attempting to streamline the user experience to eliminate any hiccups or added time to find results.
Here’s how you can optimize your content for it and stay afloat in an ever-changing search engine landscape.
Two specific ways to optimize for RankBrain
RankBrain plays a big role in how search engines filter content. According to Google representatives, it’s the third most important ranking factor.
Here are two surefire ways to keep your organic presence alive.
1. Research the intent behind every keyword.
Intent is everything when it comes to optimization and RankBrain. Machine learning has begun to understand how context plays a role in searches.
The examples we discussed earlier in this post show that intent is a big factor in search results.
If you don’t understand the searcher’s intent behind every keyword, you could be wasting tons of time and money.
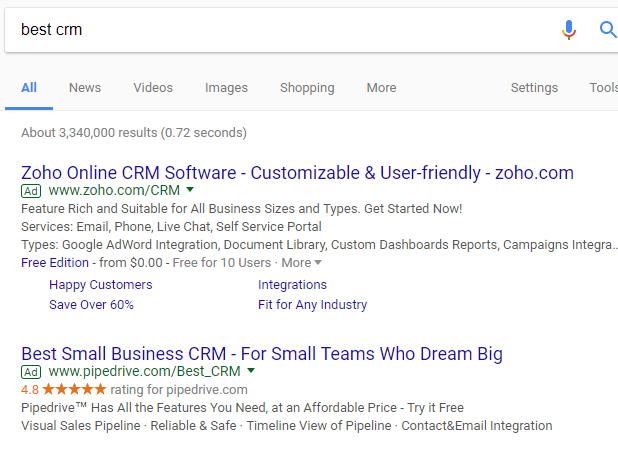
Trying to rank your CRM product for “best CRM” isn’t a good use of your efforts or budget.
Why? It’s because the intent behind the search isn’t to find a single CRM platform that claims it’s the best.
Put yourself in the user’s shoes. Let’s say you are considering purchasing a new CRM platform, but you don’t know which to choose.
You would likely search for “best crm.” The goal of that search is to see comparison articles, not a CRM company claiming to be the best.
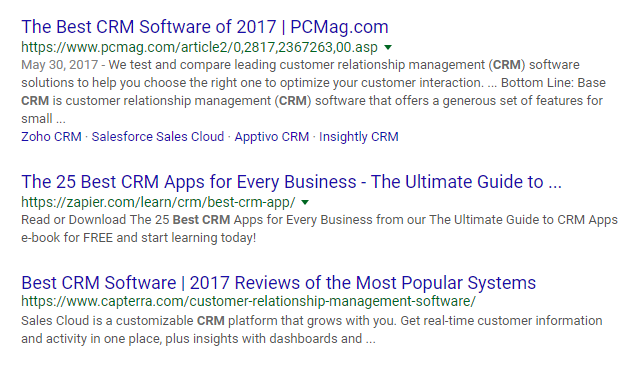
Take a look at the paid search results for “best crm:”
They don’t make sense when you factor in user intent.
Now take a look at the organic results:
Now that’s more like it. Users conducting that search most likely will want to see what types of CRMs are the best.
They want comparative data on the best options available.
Essentially, that search would fall under the consideration stage of the buyer’s journey:
The user is looking at different options to solve their pain point. They aren’t making a decision yet. If they were, they would have searched for your brand.
When you’re conducting keyword research in today’s landscape, you have to take into account user intent.
You can’t just find a popular keyword and attempt to rank for it.
Just because a keyword has 10,000 monthly searches, that doesn’t mean it’s worth your time.
To do this, you have to put yourself in the shoes of a user and explore the top-ranking content on Google for that keyword.
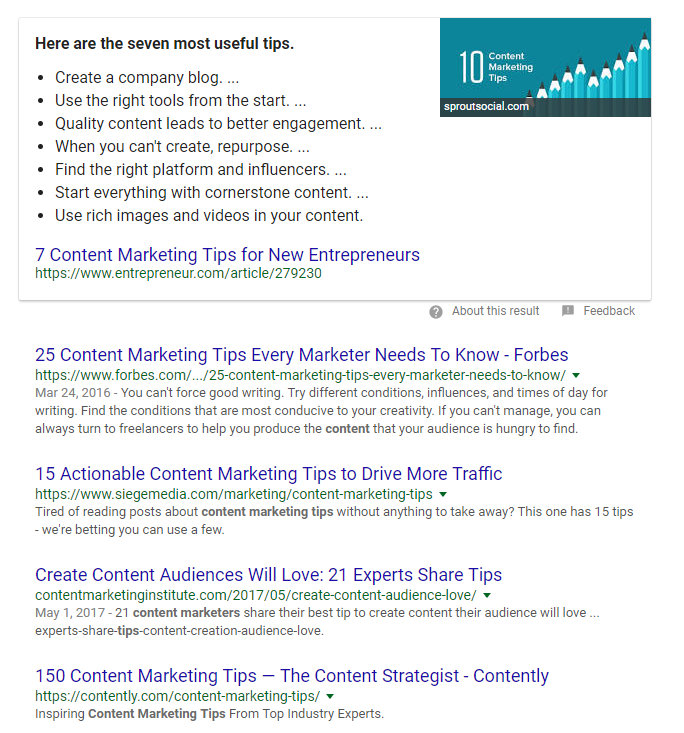
For example, let’s say you want to rank for “content marketing tips.”
What is your first guess at the most popular form or style of content that will show for this? What does the user want to see? What is the intent?
Here are the results:
If you guessed that listicle-style articles would dominate the SERPs, you were spot on.
Someone searching for “tips” is looking for multiple solutions to their problem.
They want more than one piece of actionable advice.
They want a huge list of items to view.
Another great way to decipher intent from a standard search is to scroll to the bottom of the results page and look at related searches:
These are searches where users have modified their queries after searching for the original term.
These also give you a huge insight into the intent behind their search.
Google gives us breadcrumbs along the way without ever really telling us what to do.
It’s up to us as marketers and SEOs to dive deep into their system and uncover the right data for our personal gain.
2. Craft long-form, relevant content for it.
Once you’ve researched the intent, it’s time to create content for it.
RankBrain has the same overall goal that Google has always had:
To provide the user with the content that they need on the first try.
If your content doesn’t solve the user’s problem for a given query, you aren’t going to rank for it.
It’s plain and simple. When it comes to ranking, content really is king. If your content isn’t relevant, you just won’t get traffic.
If Google knows that people didn’t find it useful, why on earth would they still include it in the search results?
They won’t.
So what does this mean for marketers? You need to create long-form content.
You need content that solves the user’s problem so well that they don’t even need to click back to Google for the next result.
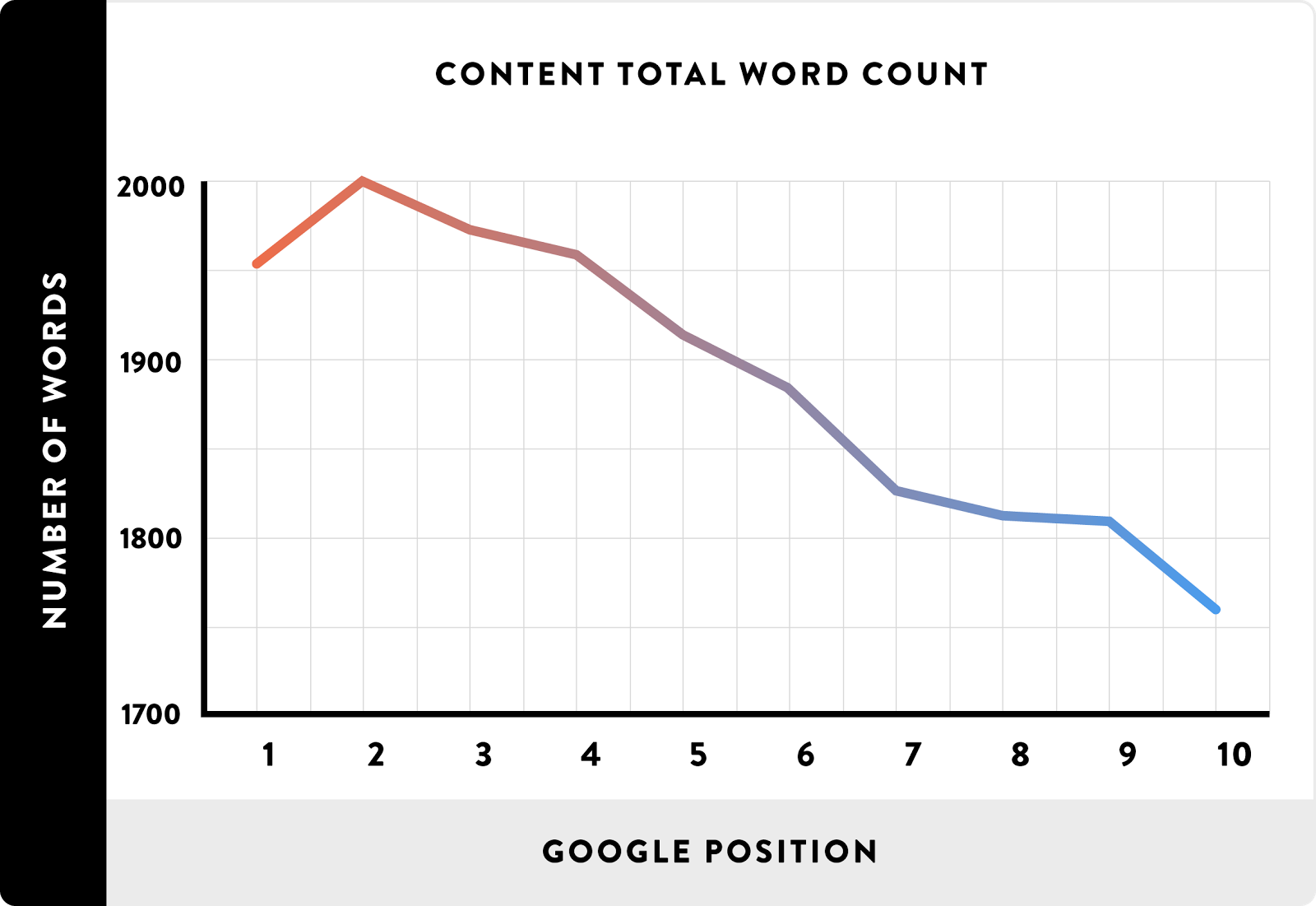
According to Backlinko, content length plays a big role in rankings:
Why is that? Well, we can infer that the word count itself isn’t necessarily driving rankings.
Writing for the sake of word count isn’t a ranking factor.
You can’t write nonsense that’s 100,000 words long and expect the #1 position.
It’s all about the value of that content.
Most long-form content is long because it packs actionable data into every sentence. It contains things like tutorials, walkthroughs, and step-by-step instructions on fixing a problem:
The more actionable you can make your piece, the better it will rank.
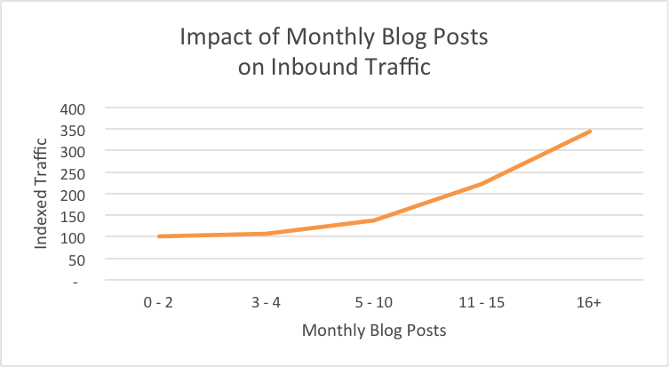
HubSpot also found that the more you post, the more traffic you get:
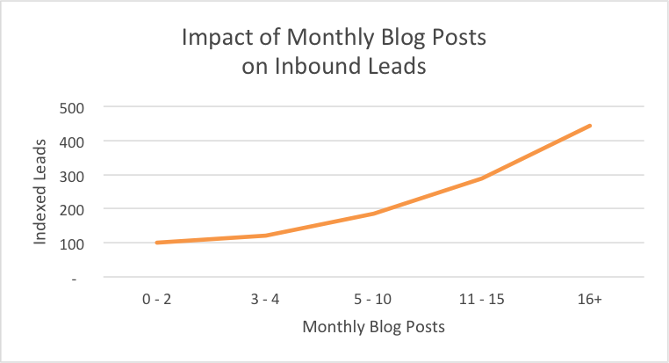
And more blog posts also means more leads:
If you focus on creating content designed for a real user experience, you will surely see improvements in your traffic.
Put yourself in a searcher’s shoes.
When you search for “how to optimize my homepage,” do you want to read a 500-word article with no images or instructions?
You obviously don’t. You want detailed steps on how to complete the task.
The moral of the story is:
Give the user what they want!
If you can research the intent behind keywords and then deliver long-form content that matches the intent, you can successfully stay afloat despite RankBrain’s meddling in our search results.
Conclusion
The headlines constantly make us think that SEO is dead. They make it sound like SEO is finished and we can’t expect organic traffic to be reliable forever.
I’ve read a few articles in just the last few months that proclaim the death of search engine optimization.
But in my opinion, it’s nowhere close to being dead.
I am still reaping the rewards of organic-based traffic on my site every day.
But Google changes their algorithm nearly two times per day and almost 600 times per year.
It’s becoming almost impossible to understand what Google wants us to do when it comes to SEO.
The top two ranking factors are still content and links, but we don’t even know what order they’re in.
Google keeps us on our toes, which makes it difficult for us to do our jobs.
Do meta descriptions matter? What kind of links should we get? What keywords still work?
We have enough questions for Google to fill an entire textbook.
And in 2015, they released even more news about RankBrain, the new AI and machine-learning technology that would filter our search results.
RankBrain is a machine-learning system that allows Google to give context to complex search queries.
You should care about it because it’s slowly becoming one of the most important ranking factors.
Thankfully, you can optimize your content for RankBrain.
Start by researching the intent behind every keyword. If you simply add keywords that you want to rank for, it won’t work.
RankBrain knows what content is right for the searcher’s intent.
Then, make great content for that keyword. Make it relevant and optimized to solve the user’s problem.
RankBrain is just the first step in the future of Google’s ranking factors. It’s time to jump ship and start optimizing.
How have you optimized your site and content marketing for RankBrain?







Comments (74)