Would you like to achieve more in less time and with less effort?
The success of any online business depends on how quickly it can turn insights into action. This is true for data analysis as well.
The good news is that you are about to learn 15 actionable tips you can use with Google Analytics to speed up your data analysis and website optimization. Apply the tips to your business, and you will improve your chances of outperforming your competitors.
Google Analytics Settings
Here is a list of things you definitely need to set up or apply in Google Analytics first:
1. Goals and Goal Values
In my experience, goals are among the most important features to set up in Google Analytics. Unfortunately, there are many websites with insufficient or incorrect goal settings.
Goals are required in order to see your conversion reports. The reports include the absolute number of conversions, conversion rate per goal, and goal value (if applied).
Google Analytics reports contain an ABC structure: (A)cquisition, (B)ehavior, and (C)onversions. For the best view, I have included only two conversion metrics in the screenshot above.
An important concept to understand is the difference between micro and macro goals and why you need them both.
“The primary goal or conversion on a website is called a “macro goal” or “macro conversion.” This could be [a visitor] making a purchase, sending in a lead gen form, making a dealer appointment, etc. It’s all about your most important business goal.”
“The secondary goals of a website are called “micro goals.” Think about [a visitor] downloading a brochure, watching a demo, or asking for more information. Most often, there is a direct relationship between your micro goals and your macro goal.”
Three Benefits of Setting Both Micro and Macro Goals
- Your website optimization potential is greater than if you set up only a primary website goal.
- You can report, analyze, and optimize interesting numbers for different departments.
- You can more easily develop a multi-channel strategy that involves both macro and micro goals.
How to Set Up a Goal
There is one prerequisite here. You need to have “edit permission rights” in Google Analytics to set up a new goal.
Also, remember that you always define a goal on the View level.
Here is a four-step short guide on how to set up a new goal:
- Sign in to Google Analytics.
- Click Admin, and navigate to the desired view.
- In the VIEW column, click Goals.
- Click + NEW GOAL or Import from Gallery to create a new goal, or click an existing goal to edit its configuration.
2. Google Analytics Annotations
If you are like me, you not only care about the “what,” but even more about the “why” and “how” behind data analysis.
This is where annotations come in handy.
Annotations in Google Analytics help you answer questions like:
“Conversions were 50% below our 12-month average during the last weekend. Was there an issue with the technical performance of our website?”
“A 400% increase in overall website traffic; how could that happen? Wait, one of our blog posts was shared by the official Google Analytics Twitter and Google + accounts, and that caused an enormous spike in our traffic figures!”
Why You Should Care about Annotations
Annotations in Google Analytics will make your life as an analyst a bit easier.
There are offline campaigns that have an impact on overall traffic.
For example, competitors that temporarily lower their prices probably influence your conversion rate and many more e-commerce metrics at the same time.
I recommend that you take a structured approach to adding “big” events to your Google Analytics account in the form of annotations.
In small organizations, this can be done by one person.
However, if you work in a large corporate business, you definitely need another approach. You could use a Google doc that one or two people in each department have access to. Or, you may already have a standard procedure for logging everything.
The more information that is known to you and your team (and that is well documented), the better the analysis and advice can be.
Many analytics audits are a nightmare simply because of poor documentation.
How to Create Annotations
You can create and add annotations via the reporting or admin interface.
Annotations via Google Analytics Reporting Interface
As a first step, navigate to any of your Google Analytics overview reports. An example is shown below:
Select the small arrow in the middle and click on the “create new annotation” link on the right.
This is the screen you will see next:
A couple of things to note here:
- Click the “star” if you want to save this annotation as one of your favorite ones. It’s easier to find your most important annotations at a later time.
- Click the correct date for your annotation (it’s not possible to add annotations for future dates).
- Choose between shared and private; most often, you will want to select “shared.” Then, other people who have access to the same reporting view can see the annotation as well.
- You can use up to 160 characters (including spaces) for your annotation.
Annotations via Google Analytics Admin Interface
I prefer to add annotations via the admin interface, especially when I need to add a couple of annotations at once.
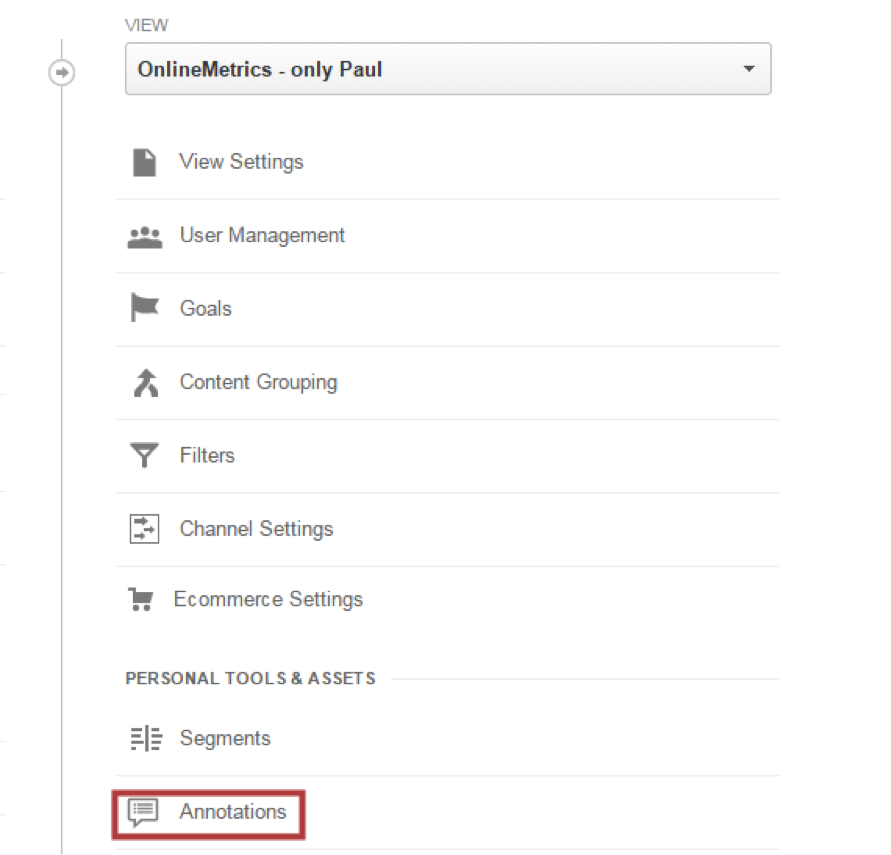
Navigate to the admin interface and click on “Annotations” (under the Personal Tools and Assets menu):
Click the new annotation link on the next screen.
Here, you can specify all the information for your annotation:
Now, it’s a vertical view compared to the horizontal view in the reporting interface. For the rest, it’s all the same.
Note: Via the admin interface, you can add annotations for future dates as well.
What to Annotate
I advise you to use annotations to keep track of everything that might impact your business.
The larger the company, the larger the number of annotations you might want to add. So, be a bit careful here not to add the tiny details to your account.
Here are five examples:
- Weather extremes
- Competitor promotions
- Offline campaigns that have a significant impact
- Industry developments
- Tracking issues
Note: Annotations set by a former employee, who no longer has access to your Google Analytics (GA) account, remain in your account.
Intelligence Events
Intelligence events are extremely useful for connecting the dots.
I like to describe intelligence events as:
“Data-driven advice by Google Analytics that helps you identify known unknowns and unknown unknowns within your data.”
I recommend that you check out these videos by Avinash Kaushik to learn more about this neat feature and terminology.
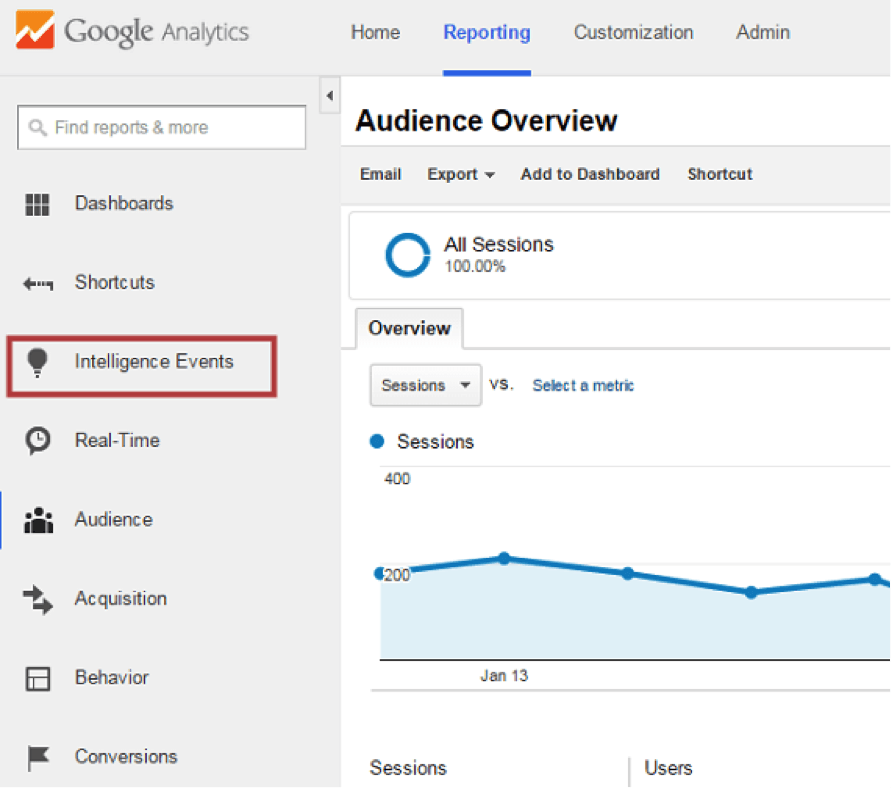
Intelligence events can be found through the reporting interface:
In Google Analytics, there are two types of intelligence events:
- Automatic alerts
- Custom alerts
Automatic alerts are created for you:
Custom alerts need to be created by you.
You need to set them up via the admin interface; it’s under the Personal Tools and Assets menu.
There are a number of things to set up:
- Alert name: an easy name to remember
- Apply to: select one or more reporting views
- Period: day, week, or month
- Email alert: you can include other people who have access to this view
- Mobile phone alert: only works if you live in the United States
- Applies to: the segment you like to apply the alert to
- Alert condition: specify when the alert needs to be triggered
I recommend that you set up at least three custom alerts:
- Traffic level
- (Macro) conversion level
- (Macro) conversion rate level
Do you need some inspiration for setting up powerful custom alerts? Check out this comprehensive list of 55+ custom alerts by LunaMetrics.
In my experience, this is one of the greatest Google Analytics shortcuts for boosting your analytics insights.
Unfortunately, it is still rarely used by most Google Analytics users.
Custom Segments to Enhance Your Insights
In the last 10, I have emphasized many times that averages lie.
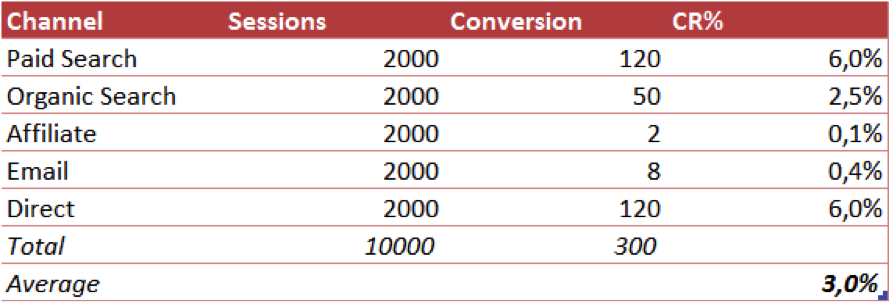
Here is a simple example:
There are a few things to note:
- Overall, this website has a conversion rate (CR) of 3.0% (not that bad!).
- Affiliate and email are performing very badly, with CR’s of 0.1% and 0.4%.
- Paid campaigns and direct traffic boost the CR.
In this case, two channels are really ruining your conversion rate. That’s why you always need to segment your data, no matter what metric you are checking.
You could do much better by improving email and affiliate channels and/or adapting your online marketing strategy.
Google Analytics has a feature called segments (advanced segments in the past). There are default and custom segments.
Default Segments
By default, Google Analytics has installed 20+ segments, of which one equals all sessions.
By hovering over a segment with your mouse, you can see the details. For example:
- Made a Purchase = segment where, at the session level, there is at least one transaction. This segment includes sessions with a purchase.
This is a great start if you are new to segments, but sometimes you just need something different.
That’s when custom segments rock!
How to Set Up Custom Segments
You can set up segments via the admin interface and reporting interface.
Segments via Google Analytics Admin Interface
- Navigate to Admin Interface.
- Head over to Personal Tools and Assets and click on Segments.
- Click on the red New Segment button.
You can set up a segment on a huge range of requirements, which are shown on the left.
Further, you have three options for segment availability.
I recommend that you carefully read the instructions by clicking on the question marks (?).
Segments via Google Analytics Reporting Interface
There is another option, which is to build your segments directly via the reporting interface:
- Navigate to a report where you can create and apply segments (e.g., Acquisition Overview).
- Click on All Sessions.
- Click on the red New Segment button.
Within the reporting interface, you have the same choices as in the admin interface.
Here are three additional points:
- Segments are linked to your unique login account information.
- Segments can be shared with other people who have access to the same view.
- You can’t apply segments to your funnel reports (PadiTrack might come in handy here).
Useful Segments to Start With
Here are ten quick ideas for segmenting your Conversion Rate (CR) and improving your insights:
- Segment your CR by device (mobile, tablet, desktop).
- Segment your CR by traffic channel.
- Segment your CR by landing page.
- Segment your CR by type of visitor (new, returning).
- Segment your CR by browser type.
- Segment your CR by geographical region.
- Segment your channel CR by attribution model.
- Segment your CR by day of week.
- Segment your CR by time of day.
- Segment your CR by campaign.
Regular Expressions
Regular expressions are incredibly useful. Here is a short overview for those who are already familiar with them:
You can effectively use them for the following:
- When setting up report filters
- When setting up goals
- When defining funnel steps
- When setting up segments
- When filtering on and analyzing your data
It really helps you to build segments and analyze subsets of data in a much faster way!
I recommend that you check out this Regular Expressions eBook from LunaMetrics if you want to learn all about regular expressions.
Campaign Tracking and Reporting
The next five tips are about how to optimize your campaign tracking and reporting efforts to save time for data analysis and website optimization.
Automate Google Analytics Campaign Tracking
Your data doesn’t have any meaning if you haven’t implemented campaign tracking in the correct way.
By default, Google Analytics recognizes three channels. On the medium level, those are:
- (None): direct traffic via bookmarks or directly typing in a URL
- Referral: incoming (untagged) links from other domains
- Organic: organic traffic via search engines
A fourth could be Google AdWords. This one is easy to set up if you link your AdWords to your Google Analytics account.
But, what about email, affiliate campaigns, or paid banners on other domains? This is where campaign tracking is crucial for getting your numbers right.
Very often, websites tend to have large buckets of direct traffic. And, do you know why? It’s because of untagged campaigns… And, it’s a disaster!
There is a huge chance that you will make the wrong decisions in your website optimization efforts. Happily, it’s easy to prevent this from happening.
Five Parameters
Google Analytics distinguishes among five parameters for campaign tracking purposes:
- Campaign Source (utm_source)
- Campaign Medium (utm_medium)
- Campaign Term (utm_term)
- Campaign Content (utm_content)
- Campaign Name (utm_campaign)
Google Analytics likes for you to always use Campaign Source, Medium, and Name when tracking “unknown” links.
Every link that does not fall into one of the four default categories needs to be tracked separately.
How to Track Campaigns
If you have just a few links you need to track, I recommend that you use the Google URL builder.
It’s a completely different story if you need to track dozens or maybe even hundreds of different campaign links.
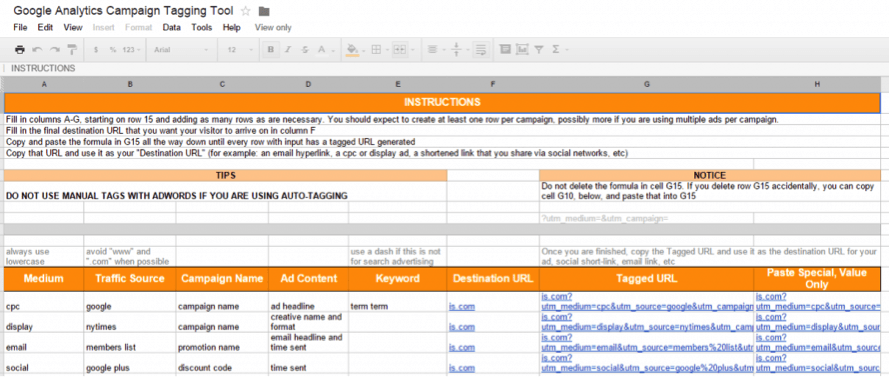
In this case, you will want to use a spreadsheet.
A good option is to use Google Docs.
Here is an example (click on image to navigate to Google Sheet):
Get access to Campaign Tracking Sheet.
My advice is to read the “Instructions” tab first.
After that, you can start experimenting with the “Link Tag Generator.”
If you have some experience, you should design a format that works for you.
I recommend that you add a few extra fields to your spreadsheet:
- Campaign period (when does your campaign run?)
- Campaign owner (who is end responsible for the campaign?)
- Naming conventions (it is a must to create a naming structure for your campaigns)
Real-Time Reports
There is one more thing you should know. I recommend that you test every link you want to track, especially if you are just starting out with campaign tracking.
It’s easy to do if you set up a view with an include filter on your IP address. If your website receives a lot of traffic, this is definitely a must to test your campaigns without effort.
And, the good thing is, you can even test in real-time. There is no need to wait until the actual data is coming in.
It’s a huge time-saver if you set this up in an efficient way! And, it makes your analysis a lot more easy and accurate.
Make sure campaign tracking is on your to-do list!
Automate Google Analytics Reporting
It’s important to report on the main KPIs of your business. However, it shouldn’t eat up all your time!
From experience, I can say that automating your reporting efforts will save a huge amount of time.
A lot of companies still need to switch from 80/20 to 20/80 in terms of reporting vs. analysis.
Automation via Google Analytics Spreadsheets Add-on
The Google Sheets Add-on helps you automatically export complex data queries. It’s a great option if you are looking for a free solution.
Make sure to check these links:
How it Works
Add the Google Analytics Add-on to Google Sheets (in my case, it is already installed).
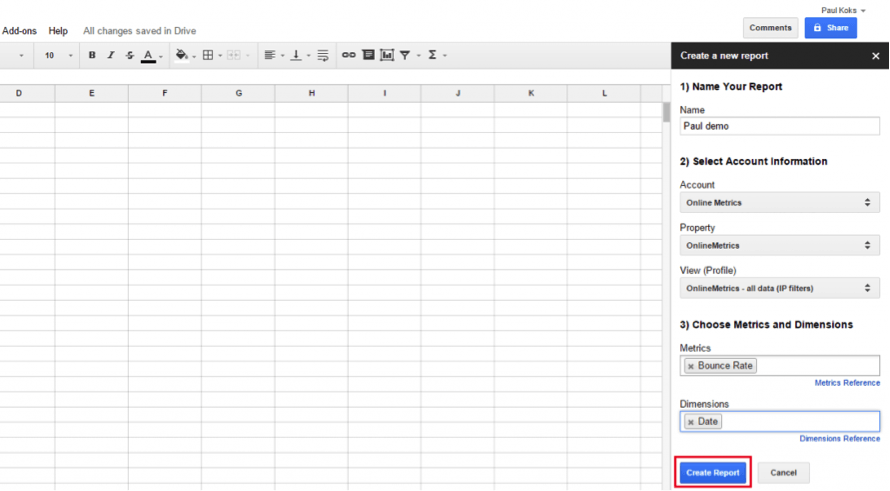
Create your first report.
- Fill in some basic information, including metrics and dimensions you like to work with.
Fill in the required fields/information:
- Report name
- Google Analytics Account name
- Google Analytics Property name
- Google Analytics View name
- One or more metrics
- One or more dimensions
Add a report name and hit Run reports on the next screen.
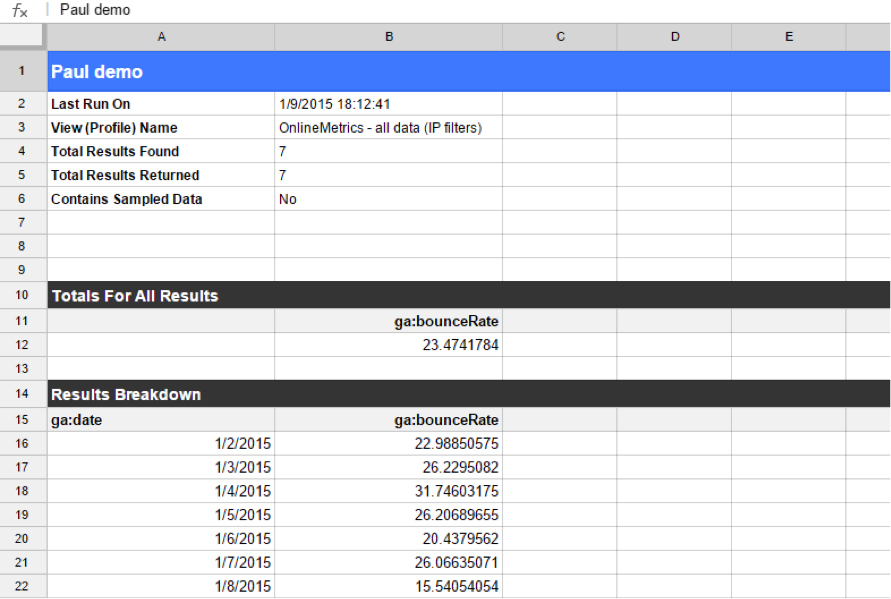
And, your report is right here!
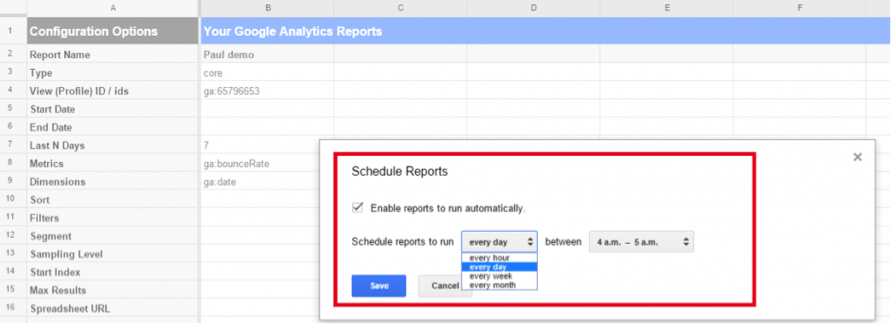
As a final step, you can schedule your report for updates.
By now, you have learned how to build a basic report via the Google Analytics application programming interface (API) and Google Sheets.
I recommend that you start with simple queries.
The Google Analytics Reference Guide shows you what functions to put in the corresponding fields.
Further, I recommend that you check out the metrics and dimensions guide. It contains all the metrics and dimensions that are available in Google Analytics.
There is a huge win in automating your data export (and dashboards), and it saves time for data analysis and website optimization.
Build Powerful Custom Reports
Another Google Analytics shortcut worth mentioning is custom reports.
You very often need to combine the information of different reports to get a clear picture of what’s going on. There are 80+ standard reports in Google Analytics, and the list is growing.
But, there is a better way: custom reports.
Custom reports help you to see your most important metrics and dimensions in one report.
Turn Standard Reports into Custom Reports
This is a great trick, especially if you are new to custom reports.
Most standard reports can function as a template for customized reports.
Click on the customize button of a standard report.
Review the metrics and dimensions of the report.
Finally, name your new custom report and click “save.”
It’s a quick way to build custom reports based on already available reports in Google Analytics.
After a while, you might want to build them from scratch as well.
Share Your Reports with Your Team
Would you like to share your reports with your team?
Great! This is very easy in Google Analytics.
Click on the Customization tab.
On the right of your screen, there is a link named Actions; click on Share.. Then select Share template link, and click Share.
This is it! By following the link, your colleagues have access to the same report. They can save it in their account.
Use Pre-Built Dashboards for Generating Ideas
Some people prefer to work with Google Analytics dashboards.
If you would like to set up your dashboard in Google Analytics, there are two resources you don’t want to miss:
- Google Analytics Solution Gallery (you can also find custom reports and segments here)
- Dashboard Junkie
Once again, you can save a lot of time that you can invest in data analysis and website optimization instead.
Copy Your Reporting Screen URL
Imagine you are working in your report and suddenly you hit the wrong button and your report and settings are lost.
Here is what I suggest to overcome this issue:
- Copy the URL of your report.
- Open another tab, screen, or notepad.
- Paste the URL.
This is especially helpful when conducting deeper analysis with advanced table filters or regular expressions.
You can also use this if you would like to perform another type of analysis for the same data set so that you can compare them.
This is another timesaver that might come in handy!
Features in Google Analytics
Google Analytics contains a lot of hidden features. The next five tips describe features that should be on your list if you want to “create” more time.
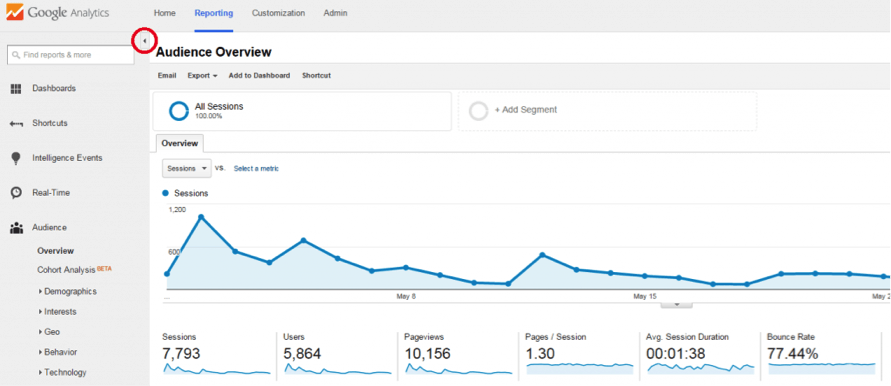
Enlarge Your Screen
This is a great tip if you want some more space to work in or if you want to avoid distractions.
Here is the default reporting view:
The left sidebar (where you can choose your favorite report) is still visible here.
If you want to minimize distractions and maximize your view, click the small arrow shown above (in red).
As you can see, your reporting screen becomes much wider.
I find it very helpful in two situations:
- When I’m working in a large report and want to have enough space to analyze all the data; e.g., I’ve built a custom flat table with 3+ dimensions and quite a few metrics.
- When I’m presenting / giving a Google Analytics workshop and want to avoid any distractions.
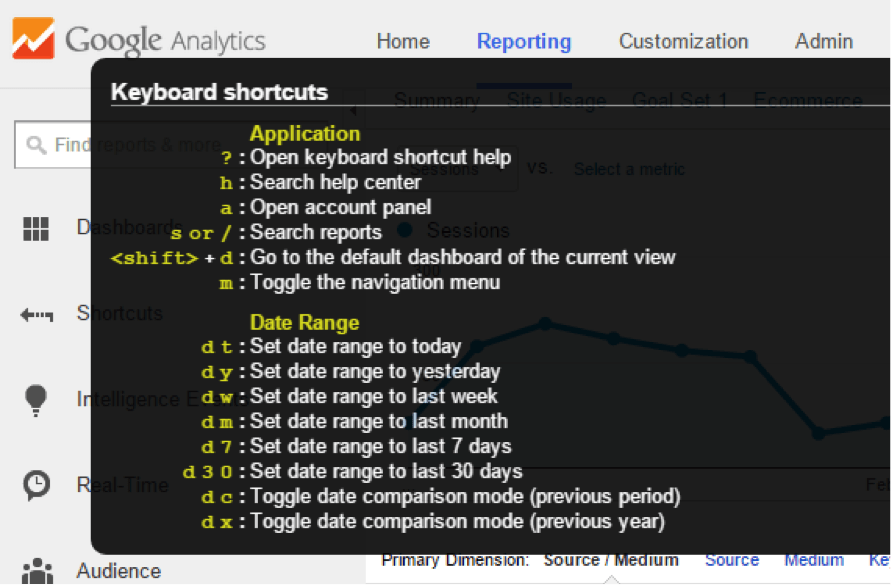
Memorize Basic Keyboard Shortcuts
Navigate to the reporting interface and hit question mark (?).
The following screen pops up:
I find the date range shortcuts to be very useful. You can quickly select the desired data set without touching your mouse.
Most analysts could save quite some time by using these hidden keyboard shortcuts.
In my experience, it is also great if you quickly jump around and present useful data to your audience.
Save Report Shortcuts
The Google Analytics Shortcuts feature is very powerful.
It allows you to save your favorite reports with all settings included.
Here is how it works:
Step 1. Select the report and all settings you would like to save.
Step 2. Click Shortcut and add a unique shortcut name.
Step 3. Click on the Shortcut name in the report view to access it.
It’s easy, fast, and very handy; really useful for everyone who works with Google Analytics.
Also, this is a must have for consultants who are working with many websites. You can save your favorite reports and settings for each of your clients in their specific accounts.
Use “Find Reports & More” Module
Do you sometimes struggle with finding the report you need? You know its name but have forgotten exactly where it’s located.
No need to worry, the find reports & more function comes in handy here!
Take a look at the screenshot below:
This feature applies to three different reports/features:
- Standard reports
- Custom reports
- Shortcuts (to favorite reporting settings)
Type in the first few characters, and you should be able to find your report.
It’s another smart way to quickly navigate through Google Analytics.
BONUS
Always Start with a Question in Mind
I strongly recommend that you come up with a business question first before diving into Google Analytics or any other web analytics tool.
Your business question should be connected to one or more of your micro or macro goals (discussed in the first tip).
If you don’t know what you need to solve, how can you decide where to start? It’s simply impossible.
You can literally lose days of time if you don’t take a structured approach in your data analysis and website optimization efforts.
Conclusion
A thorough analysis of your Google Analytics data is a must to derive great insights.
Most importantly, be sure to collect and analyze the data that really matters to the success of your online business.
Apply the 15 Google Analytics tips in this post to boost your data analysis and website optimization efforts.
What did I miss? Do you use other tactics to speed up your data analysis and get the most out of Google Analytics?
About the Author: Paul Koks is a passionate Analytics and Optimization Consultant. He specializes in helping companies analyze and optimize their websites and traffic channels. On his website Online-Metrics.com, he shares actionable insights and best practices on Google Analytics and Conversion Optimization. Connect with him via Twitter: @OnlineMetrics.














Comments (12)